Dynamical modeling of miR-34a, miR-449a, and miR-16 reveals numerous DDR signaling pathways regulating senescence, autophagy, and apoptosis in HeLa cells
- PMID: 35318393
- PMCID: PMC8941124
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08900-y
Dynamical modeling of miR-34a, miR-449a, and miR-16 reveals numerous DDR signaling pathways regulating senescence, autophagy, and apoptosis in HeLa cells
Abstract
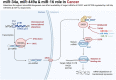
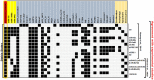
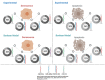
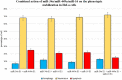
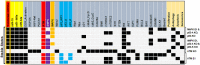
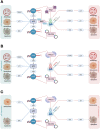
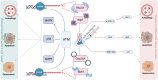
Transfection of tumor suppressor miRNAs such as miR-34a, miR-449a, and miR-16 with DNA damage can regulate apoptosis and senescence in cancer cells. miR-16 has been shown to influence autophagy in cervical cancer. However, the function of miR-34a and miR-449a in autophagy remains unknown. The functional and persistent G1/S checkpoint signaling pathways in HeLa cells via these three miRNAs, either synergistically or separately, remain a mystery. As a result, we present a synthetic Boolean network of the functional G1/S checkpoint regulation, illustrating the regulatory effects of these three miRNAs. To our knowledge, this is the first synthetic Boolean network that demonstrates the advanced role of these miRNAs in cervical cancer signaling pathways reliant on or independent of p53, such as MAPK or AMPK. We compared our estimated probability to the experimental data and found reasonable agreement. Our findings indicate that miR-34a or miR-16 may control senescence, autophagy, apoptosis, and the functional G1/S checkpoint. Additionally, miR-449a can regulate just senescence and apoptosis on an individual basis. MiR-449a can coordinate autophagy in HeLa cells in a synergistic manner with miR-16 and/or miR-34a.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of hsa-miR-34a and hsa-miR-449a leads to overexpression of PACS-1 and loss of DNA damage response (DDR) in cervical cancer.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 11;295(50):17169-17186. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014048. Epub 2020 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33028635 Free PMC article.
-
ATM/miR-34a-5p axis regulates a p21-dependent senescence-apoptosis switch in non-small cell lung cancer: a Boolean model of G1/S checkpoint regulation.FEBS Lett. 2020 Jan;594(2):227-239. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13615. Epub 2019 Oct 10. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 31545515
-
Towards DNA-damage induced autophagy: A Boolean model of p53-induced cell fate mechanisms.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Dec;96:102971. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102971. Epub 2020 Sep 11. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32987354
-
MicroRNAs as biomarkers of cervical cancer development: a literature review on miR-125b and miR-34a.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Mar;41(3):1525-31. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2998-0. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24402874 Review.
-
Expanding the Biotherapeutics Realm via miR-34a: "Potent Clever Little" Agent in Breast Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(8):665-673. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190617162042. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31244419 Review.
Cited by
-
Quadra-Stable Dynamics of p53 and PTEN in the DNA Damage Response.Cells. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):1085. doi: 10.3390/cells12071085. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048159 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Autophagy-related miRNAs in Gynecologic Tumors: A Review of Current Knowledge for Possible Targeted Therapy.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(10):1269-1281. doi: 10.2174/0115665240263059231002093454. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39300715 Review.
-
LncRNA PTENP1/miR-21/PTEN Axis Modulates EMT and Drug Resistance in Cancer: Dynamic Boolean Modeling for Cell Fates in DNA Damage Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 29;25(15):8264. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158264. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125832 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles and Potential Applications of Non-Coding RNAs in Cervical Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;13(7):1254. doi: 10.3390/genes13071254. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35886037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification of Chest CT Lung Nodules Using Collaborative Deep Learning Model.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Apr 4;17:1459-1472. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S456167. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38596001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Veena MS, Raychaudhuri S, Basak SK, Venkatesan N, Kumar P, Biswas R, Chakrabarti R, Lu J, Su T, Gallagher-Jones M, Morselli M, Fu H, Pellegrini M, Goldstein T, Aladjem MI, Rettig MB, Wilczynski SP, Shin DS, Srivatsan ES. Dysregulation of hsa-miR-34a and hsa-miR-449a leads to overexpression of PACS-1 and loss of DNA damage response (DDR) in cervical cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2020;295:17169–17186. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi DW, Na W, Kabir MH, Yi E, Kwon S, Yeom J, Ahn J-W, Choi H-H, Lee Y, Seo KW, Shin MK, Park S-H, Yoo HY, Isono K-I, Koseki H, Kim S-T, Lee C, Kwon YK, Choi CY. WIP1, a homeostatic regulator of the DNA damage response, is targeted by HIPK2 for phosphorylation and degradation. Mol. Cell. 2013;51:374–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

