Computed tomography and [18F]-FDG PET imaging provide additional readouts for COVID-19 pathogenesis and therapies evaluation in non-human primates
- PMID: 35313622
- PMCID: PMC8926429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104101
Computed tomography and [18F]-FDG PET imaging provide additional readouts for COVID-19 pathogenesis and therapies evaluation in non-human primates
Abstract
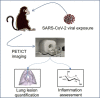
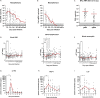
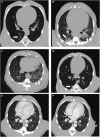
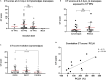
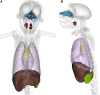
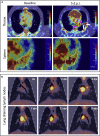
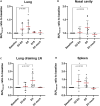
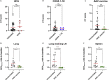
Non-human primates (NHPs) are particularly relevant as preclinical models for SARS-CoV-2 infection and nuclear imaging may represent a valuable tool for monitoring infection in this species. We investigated the benefit of computed X-ray tomography (CT) and [18F]-FDG positron emission tomography (PET) to monitor the early phase of the disease in a large cohort (n = 76) of SARS-CoV-2 infected macaques. Following infection, animals showed mild COVID-19 symptoms including typical lung lesions. CT scores at the acute phase reflect the heterogeneity of lung burden following infection. Moreover, [18F]-FDG PET revealed that FDG uptake was significantly higher in the lungs, nasal cavities, lung-draining lymph nodes, and spleen of NHPs by 5 days postinfection compared to pre-infection levels, indicating early local inflammation. The comparison of CT and PET data from previous COVID-19 treatments or vaccines we tested in NHP, to this large cohort of untreated animals demonstrated the value of in vivo imaging in preclinical trials.
Keywords: Medical imaging; Medical microbiology; Virology.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
Vasculitis changes in COVID-19 survivors with persistent symptoms: an [18F]FDG-PET/CT study.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 May;48(5):1460-1466. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-05084-3. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33123760 Free PMC article.
-
Increased incidence of interstitial pneumonia detected on [18F]-FDG-PET/CT in asymptomatic cancer patients during COVID-19 pandemic in Lombardy: a casualty or COVID-19 infection?Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Mar;48(3):777-785. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-05027-y. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 32909090 Free PMC article.
-
The value of FDG positron emission tomography/computerised tomography (PET/CT) in pre-operative staging of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Sep;15(35):1-192, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta15350. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21958472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of 2-[18F]FDG as a Radiopharmaceutical for PET/CT in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Nov 10;13(11):377. doi: 10.3390/ph13110377. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33182811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity and efficacy of VLA2001 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infection in male cynomolgus macaques.Commun Med (Lond). 2024 Apr 3;4(1):62. doi: 10.1038/s43856-024-00488-w. Commun Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38570605 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-related bat virus behavior in human-relevant models sheds light on the origin of COVID-19.EMBO Rep. 2023 Apr 5;24(4):e56055. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256055. Epub 2023 Mar 6. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 36876574 Free PMC article.
-
BioSimia, France CNRS network for nonhuman primate biomedical research in infectiology, immunology, and neuroscience.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022 Sep 2;3:100051. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2022.100051. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36685763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broadly neutralizing humanized SARS-CoV-2 antibody binds to a conserved epitope on Spike and provides antiviral protection through inhalation-based delivery in non-human primates.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 2;19(8):e1011532. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011532. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37531329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albarello F., Pianura E., Di Stefano F., Cristofaro M., Petrone A., Marchioni L., Palazzolo C., Schinina V., Nicastri E., Petrosillo N., et al. 2019-novel coronavirus severe adult respiratory distress syndrome in two cases in Italy: an uncommon radiological presentation. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020;93:192–197. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

