Fertilization, Oocyte Activation, Calcium Release and Epigenetic Remodelling: Lessons From Cancer Models
- PMID: 35309905
- PMCID: PMC8931327
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.781953
Fertilization, Oocyte Activation, Calcium Release and Epigenetic Remodelling: Lessons From Cancer Models
Abstract
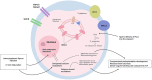
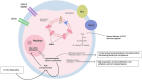
Oocyte activation deficiency (OAD) is the basis of Total Fertilisation Failure (TFF) and is attributed to mutations in the PLCζ gene-termed male factor infertility. This derives abnormal Ca2+ oscillations and could be the main cause of primary disruptions in the gene expression of Ca2+-related proteins. Epigenetic mechanisms are universally accepted as key regulators of gene expression. However, epigenetic dysregulations have not been considered as potential mechanisms of oocyte-borne OAD. Herein, we discuss changes in the DNA methylome during oogenesis and embryogenesis. We further highlight key pathways comprising the oocyte Ca2+ toolkit, which could be targets of epigenetic alterations, especially aberrations in DNA methylation. Considering that the vast majority of epigenetic modifications examined during fertilization revolve around alterations in DNA methylation, we aim in this article to associate Ca2+-specific mechanisms with these alterations. To strengthen this perspective, we bring evidence from cancer research on the intricate link between DNA methylation and Ca2+ signaling as cancer research has examined such questions in a lot more detail. From a therapeutic standpoint, if our hypothesis is proven to be correct, this will explain the cause of TFF in idiopathic cases and will open doors for novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: DNA methylation; calcium; cancer; fertlization; oocyte activation.
Copyright © 2022 Shafqat, Kashir, Alsalameh, Alkattan and Yaqinuddin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phospholipase C zeta (PLCζ) and male infertility: Clinical update and topical developments.Adv Biol Regul. 2016 May;61:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.11.009. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Adv Biol Regul. 2016. PMID: 26700242 Review.
-
Oocyte activation deficiency and assisted oocyte activation: mechanisms, obstacles and prospects for clinical application.Hum Reprod Open. 2022 Feb 7;2022(2):hoac003. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoac003. eCollection 2022. Hum Reprod Open. 2022. PMID: 35261925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic and Diagnostic Potential of Phospholipase C Zeta, Oocyte Activation, and Calcium in Treating Human Infertility.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;16(3):441. doi: 10.3390/ph16030441. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase C zeta (PLCζ): oocyte activation and clinical links to male factor infertility.Adv Biol Regul. 2013 Sep;53(3):292-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2013.07.005. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Adv Biol Regul. 2013. PMID: 23916605 Review.
-
Artificial oocyte activation: physiological, pathophysiological and ethical aspects.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019 Feb;65(1):3-11. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1516000. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 30207496 Review.
Cited by
-
Preimplantation Developmental Competence of Bovine and Porcine Oocytes Activated by Zinc Chelation.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;12(24):3560. doi: 10.3390/ani12243560. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552480 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensively analyzing the genetic alterations, and identifying key genes in ovarian cancer.Oncol Res. 2023 Apr 10;31(2):141-156. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.028548. eCollection 2023. Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37304238 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA Methylation Perspective on Infertility.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;14(12):2132. doi: 10.3390/genes14122132. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reproductive Consequences of Electrolyte Disturbances in Domestic Animals.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 3;11(7):1006. doi: 10.3390/biology11071006. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36101387 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

