Celastrol Downmodulates Alpha-Synuclein-Specific T Cell Responses by Mediating Antigen Trafficking in Dendritic Cells
- PMID: 35309340
- PMCID: PMC8926036
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.833515
Celastrol Downmodulates Alpha-Synuclein-Specific T Cell Responses by Mediating Antigen Trafficking in Dendritic Cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Celastrol Downmodulates Alpha-Synuclein-Specific T Cell Responses by Mediating Antigen Trafficking in Dendritic Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 May 20;13:907993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907993. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35669764 Free PMC article.
Abstract
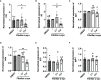
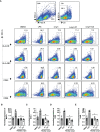
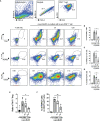
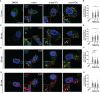
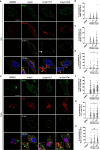
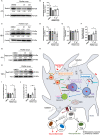
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease that affects the elderly. It is associated with motor dysfunction due to the accumulation of misfolded or aggregated fibrillar alpha-synuclein (α-syn) in the mid-brain. Current treatments are mainly focused on relieving the symptoms but are accompanied by side effects and are limited in halting disease progression. Increasing evidence points to peripheral immune cells underlying disease development, especially T cells contributing to α-syn-related neuroinflammation in PD. The onset of these cells is likely mediated by dendritic cells (DCs), whose role in α-syn-specific responses remain less studied. Moreover, Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)-derived compounds that are candidates to treat PD may alleviate DC-T cell-mediated immune responses. Therefore, our study focused on the role of DC in response to fibrillar α-syn and subsequent induction of antigen-specific T cell responses, and the effect of TCM Curcumin-analog C1 and Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F-derived Celastrol. We found that although fibrillar α-syn did not induce significant inflammatory or T cell-mediating cytokines, robust pro-inflammatory T cell responses were found by co-culturing fibrillar α-syn-pulsed DCs with α-syn-specific CD4+ T cells. Celastrol, but not C1, reduced the onset of pro-inflammatory T cell differentiation, through promoting interaction of endosomal, amphisomal, and autophagic vesicles with fibrillar α-syn, which likely lead to its degradation and less antigen peptides available for presentation and T cell recognition. In conclusion, regulating the intracellular trafficking/processing of α-syn by DCs can be a potential approach to control the progression of PD, in which Celastrol is a potential candidate to accomplish this.
Keywords: CD4+ T cell subsets; Celastrol; Parkinson’s Disease; autophagy; dendritic cell; endo-lysosomal pathway; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2022 Ng, Wang, Yang, Su, Li and Cheung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astragaloside IV Inhibits Rotenone-Induced α-syn Presentation and the CD4 T-Cell Immune Response.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jan;61(1):252-265. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03566-7. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37603153
-
Targeting of the class II transactivator attenuates inflammation and neurodegeneration in an alpha-synuclein model of Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 30;15(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1286-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30165873 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum: Celastrol Downmodulates Alpha-Synuclein-Specific T Cell Responses by Mediating Antigen Trafficking in Dendritic Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 May 20;13:907993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907993. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35669764 Free PMC article.
-
A Cleaning Crew: The Pursuit of Autophagy in Parkinson's Disease.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 Sep 18;10(9):3914-3926. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00244. Epub 2019 Aug 20. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31385687 Review.
-
Alpha-Synuclein and the Endolysosomal System in Parkinson's Disease: Guilty by Association.Biomolecules. 2021 Sep 9;11(9):1333. doi: 10.3390/biom11091333. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34572546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Autoimmune Cell in DA Neuron Apoptosis of Parkinson's Disease: Recent Advancement.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Dec 14;2022:7965433. doi: 10.1155/2022/7965433. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36567855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-to-gut trafficking of alpha-synuclein by CD11c+ cells in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 20;14(1):7529. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43224-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37981650 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in the pharmacological activities of celastrol (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 20;25(6):268. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11967. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37206564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning screening for Parkinson's disease-related cuproptosis-related typing development and validation and exploration of personalized drugs for cuproptosis genes.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 15;11(1):11. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5756. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36760248 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

