Duck plague virus UL41 protein inhibits RIG-I/MDA5-mediated duck IFN-β production via mRNA degradation activity
- PMID: 35303942
- PMCID: PMC8932288
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-022-01043-y
Duck plague virus UL41 protein inhibits RIG-I/MDA5-mediated duck IFN-β production via mRNA degradation activity
Abstract
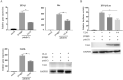
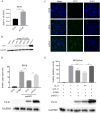
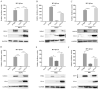
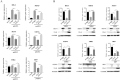
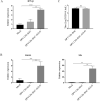
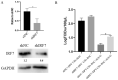
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs) are cytosolic pattern recognition receptors that initiate innate antiviral immunity. Recent reports found that duck RLRs significantly restrict duck plague virus (DPV) infection. However, the molecular mechanism by which DPV evades immune responses is unknown. In this study, we first found that the DPV UL41 protein inhibited duck interferon-β (IFN-β) production mediated by RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) by broadly downregulating the mRNA levels of important adaptor molecules, such as RIG-I, MDA5, mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein (MAVS), stimulator of interferon gene (STING), TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), and interferon regulatory factor (IRF) 7. The conserved sites of the UL41 protein, E229, D231, and D232, were responsible for this activity. Furthermore, the DPV CHv-BAC-ΔUL41 mutant virus induced more duck IFN-β and IFN-stimulated genes (Mx, OASL) production in duck embryo fibroblasts (DEFs) than DPV CHv-BAC parent virus. Our findings provide insights into the molecular mechanism underlying DPV immune evasion.
Keywords: DPV; IFN-β; RLRs; UL41 protein; innate immune response; mRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Binding of Duck Tembusu Virus Nonstructural Protein 2A to Duck STING Disrupts Induction of Its Signal Transduction Cascade To Inhibit Beta Interferon Induction.J Virol. 2020 Apr 16;94(9):e01850-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01850-19. Print 2020 Apr 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32075929 Free PMC article.
-
Duck Enteritis Virus Inhibits the cGAS-STING DNA-Sensing Pathway To Evade the Innate Immune Response.J Virol. 2022 Dec 21;96(24):e0157822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01578-22. Epub 2022 Nov 30. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36448809 Free PMC article.
-
Duck stimulator of interferon genes plays an important role in host anti-duck plague virus infection through an IFN-dependent signalling pathway.Cytokine. 2018 Feb;102:191-199. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 28969942
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs) in fish: current knowledge and future perspectives.Immunology. 2017 May;151(1):16-25. doi: 10.1111/imm.12714. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28109007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Breaking Latent Infection: How ORF37/38-Deletion Mutants Offer New Hope against EHV-1 Neuropathogenicity.Viruses. 2024 Sep 16;16(9):1472. doi: 10.3390/v16091472. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339948 Free PMC article.
-
Duck plague virus UL24 protein initiates K48/K63-linked IRF7 polyubiquitination to antagonize the innate immune response.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104378. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104378. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39418790 Free PMC article.
-
N-glycosylation of the envelope glycoprotein I is essential for the proliferation and virulence of the duck plague virus.Vet Res. 2024 Oct 26;55(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01398-4. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39462432 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of herpesvirus UL24 protein regulating viral immune escape and virulence.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 22;14:1268429. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1268429. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudorabies virus VHS protein abrogates interferon responses by blocking NF-κB and IRF3 nuclear translocation.Virol Sin. 2024 Aug;39(4):587-599. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2024.05.009. Epub 2024 May 30. Virol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38823782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jahan AS, Biquand E, Munoz-Moreno R, Le Quang A, Mok CK, Wong HH, Teo QW, Valkenburg SA, Chin AWH, Man Poon LL, Te Velthuis A, García-Sastre A, Demeret C, Sanyal S. OTUB1 is a key regulator of RIG-I-dependent immune signaling and is targeted for proteasomal degradation by influenza A NS1. Cell Rep. 2020;30:1570–1584. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

