Increased O-GlcNAcylation promotes IGF-1 receptor/PhosphatidyI Inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway in cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 35296731
- PMCID: PMC8927345
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08445-0
Increased O-GlcNAcylation promotes IGF-1 receptor/PhosphatidyI Inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway in cervical cancer cells
Abstract
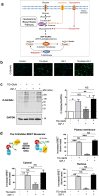
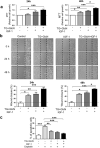
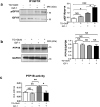
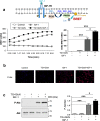
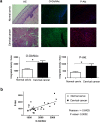
O-linked β-N-acetylglucosaminylation (O-GlcNAcylation) is a reversible post-translational modification on serine and threonine residues of cytosolic, nuclear and mitochondrial proteins. O-GlcNAcylation level is regulated by OGT (O-GlcNAc transferase), which adds GlcNAc on proteins, and OGA (O-GlcNAcase), which removes it. Abnormal level of protein O-GlcNAcylation has been observed in numerous cancer cell types, including cervical cancer cells. In the present study, we have evaluated the effect of increasing protein O-GlcNAcylation on cervical cancer-derived CaSki cells. We observed that pharmacological enhancement of protein O-GlcNAcylation by Thiamet G (an inhibitor of OGA) and glucosamine (which provides UDP-GlcNAc substrate to OGT) increases CaSki cells proliferation, migration and survival. Moreover, we showed that increased O-GlcNAcylation promotes IGF-1 receptor (IGF1R) autophosphorylation, possibly through inhibition of protein tyrosine-phosphatase 1B activity. This was associated with increased IGF-1-induced phosphatidyl-Inositol 3-phosphate production at the plasma membrane and increased Akt activation in CaSki cells. Finally, we showed that protein O-GlcNAcylation and Akt phosphorylation levels were higher in human cervical cancer samples compared to healthy cervix tissues, and a highly positive correlation was observed between O-GlcNAcylation level and Akt phosphorylation in theses tissues. Together, our results indicate that increased O-GlcNAcylation, by activating IGF1R/ Phosphatidyl inositol 3-Kinase (PI-3K)/Akt signaling, may participate in cervical cancer cell growth and proliferation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) Homeostasis Activate the p53 Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 2;291(36):18897-914. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.734533. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27402830 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of O-GlcNAcylation and involvement of PI3K/Akt1 pathway in the expression of oncogenic phenotypes of gastric cancer cells in vitro.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2016 Nov;63(6):841-851. doi: 10.1002/bab.1441. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26333304
-
O-GlcNAcylation-inducing treatments inhibit estrogen receptor α expression and confer resistance to 4-OH-tamoxifen in human breast cancer-derived MCF-7 cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 11;8(7):e69150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069150. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23935944 Free PMC article.
-
O-GlcNAcylation in cancer development and immunotherapy.Cancer Lett. 2023 Jul 10;566:216258. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216258. Epub 2023 Jun 4. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37279852 Review.
-
[Protein O-GlcNAcylation and regulation of cell signalling: involvement in pathophysiology].Biol Aujourdhui. 2014;208(2):109-17. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2014015. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Biol Aujourdhui. 2014. PMID: 25190571 Review. French.
Cited by
-
PARP1 acetylation at K119 is essential in regulating the progression and proliferation of cervical cancer cells.Med Oncol. 2024 Oct 14;41(11):273. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02315-7. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39400626
-
O-GlcNAcylation: Crosstalk between Hemostasis, Inflammation, and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 13;25(18):9896. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189896. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
O-GlcNAcylation in Renal (Patho)Physiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 24;23(19):11260. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911260. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of metabolomics in cervical cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Dec 13;28(1):586. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01490-z. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38093395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tools for investigating O-GlcNAc in signaling and other fundamental biological pathways.J Biol Chem. 2024 Feb;300(2):105615. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105615. Epub 2023 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38159850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Issad T, Kuo M. O-GlcNAc modification of transcription factors, glucose sensing and glucotoxicity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008;19:380–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

