More than Meets the Eye: The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor is an Environmental Sensor, Physiological Regulator and a Therapeutic Target in Ocular Disease
- PMID: 35295218
- PMCID: PMC8915869
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2022.791082
More than Meets the Eye: The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor is an Environmental Sensor, Physiological Regulator and a Therapeutic Target in Ocular Disease
Abstract
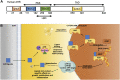
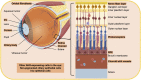
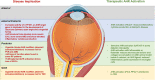
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a ligand activated transcription factor originally identified as an environmental sensor of xenobiotic chemicals. However, studies have revealed that the AHR regulates crucial aspects of cell growth and metabolism, development and the immune system. The importance of the AHR and AHR signaling in eye development, toxicology and disease is now being uncovered. The AHR is expressed in many ocular tissues including the retina, choroid, cornea and the orbit. A significant role for the AHR in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), autoimmune uveitis, and other ocular diseases has been identified. Ligands for the AHR are structurally diverse organic molecules from exogenous and endogenous sources. Natural AHR ligands include metabolites of tryptophan and byproducts of the microbiome. Xenobiotic AHR ligands include persistent environmental pollutants such as dioxins, benzo (a) pyrene [B (a) P] and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Pharmaceutical agents including the proton pump inhibitors, esomeprazole and lansoprazole, and the immunosuppressive drug, leflunomide, activate the AHR. In this review, we highlight the role of the AHR in the eye and discuss how AHR signaling is involved in responding to endogenous and environmental stimuli. We also present the emerging concept that the AHR is a promising therapeutic target for eye disease.
Keywords: 6-formylindolo (3, 2-b) carbazole; AHR (aryl hydrocarbon agonist); FICZ; TCDD (2, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo- p-dioxin); cigarette; eye; retina; thyroid eye disease (TED).
Copyright © 2022 Hammond, Roztocil, Gupta, Feldon and Woeller.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of CC-chemokine ligand 5 by aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands.J Dermatol Sci. 2013 Oct;72(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Dermatol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23810773
-
The tryptophan derivative 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole, FICZ, a dynamic mediator of endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling, balances cell growth and differentiation.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018 Aug;48(7):555-574. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2018.1493086. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30226107 Review.
-
Responsiveness of a Xenopus laevis cell line to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD).Chem Biol Interact. 2010 Jan 5;183(1):202-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2009.09.017. Chem Biol Interact. 2010. PMID: 19799885 Free PMC article.
-
Dioxins and related environmental contaminants increase TDP-43 levels.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 May 5;12(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0177-9. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28476168 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a drug target in advanced prostate cancer therapy - obstacles and perspectives.Transcription. 2024 Mar 28:1-20. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2024.2334106. Online ahead of print. Transcription. 2024. PMID: 38547312 Review.
Cited by
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6719. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126719. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Applications of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) CYP1A-Targeted Monoclonal Antibody (CRC4) with Reactivity across Vertebrate Taxa: Evidence for a Conserved CYP1A Epitope.Toxics. 2022 Jul 20;10(7):404. doi: 10.3390/toxics10070404. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35878309 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic high-throughput screening identifies aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonism as common inhibitor of toxin-induced retinal pigment epithelium cell death.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 18;19(4):e0301239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301239. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38635505 Free PMC article.
-
Light Sensing beyond Vision: Focusing on a Possible Role for the FICZ/AhR Complex in Skin Optotransduction.Cells. 2024 Jun 22;13(13):1082. doi: 10.3390/cells13131082. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) beyond the canonical AHR/ARNT signaling pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Feb;208:115371. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115371. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36528068 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Awji E. G., Chand H., Bruse S., Smith K. R., Colby J. K., Mebratu Y., et al. (2015). Wood Smoke Enhances Cigarette Smoke-Induced Inflammation by Inducing the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Repressor in Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cel Mol Biol 52, 377–386. 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0142oc - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baglole C. J., Maggirwar S. B., Gasiewicz T. A., Thatcher T. H., Phipps R. P., Sime P. J. (2008). The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Attenuates Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cyclooxygenase-2 and Prostaglandin Production in Lung Fibroblasts through Regulation of the NF-Κb Family Member RelB. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 28944–28957. 10.1074/jbc.m800685200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

