Recent Advances in Cell Therapeutics for Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 35291648
- PMCID: PMC8901702
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e10
Recent Advances in Cell Therapeutics for Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
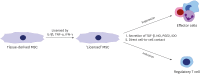
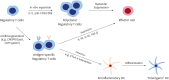
Systemic autoimmune diseases arise from loss of self-tolerance and immune homeostasis between effector and regulator functions. There are many therapeutic modalities for autoimmune diseases ranging from conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and immunosuppressants exerting nonspecific immune suppression to targeted agents including biologic agents and small molecule inhibitors aiming at specific cytokines and intracellular signal pathways. However, such current therapeutic strategies can rarely induce recovery of immune tolerance in autoimmune disease patients. To overcome limitations of conventional treatment modalities, novel approaches using specific cell populations with immune-regulatory properties have been attempted to attenuate autoimmunity. Recently progressed biotechnologies enable sufficient in vitro expansion and proper manipulation of such 'tolerogenic' cell populations to be considered for clinical application. We introduce 3 representative cell types with immunosuppressive features, including mesenchymal stromal cells, Tregs, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Their cellular definitions, characteristics, mechanisms of immune regulation, and recent data about preclinical and clinical studies in systemic autoimmune diseases are reviewed here. Challenges and limitations of each cell therapy are also addressed.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; Cell therapy; Mesenchymal stromal cells; Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; Regulatory T cells.
Copyright © 2022. The Korean Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Getting Under the Skin: Targeting Cutaneous Autoimmune Disease.Yale J Biol Med. 2020 Mar 27;93(1):197-206. eCollection 2020 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32226348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three distinct tolerogenic CD14+ myeloid cell types to actively manage autoimmune disease: Opportunities and challenges.J Autoimmun. 2021 Jun;120:102645. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102645. Epub 2021 Apr 23. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33901801 Review.
-
Restoring self-tolerance in autoimmune diseases by enhancing regulatory T-cells.Cell Immunol. 2019 May;339:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Cell Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30482489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerising cellular therapies: what is their promise for autoimmune disease?Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar;78(3):297-310. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214024. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30389690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerizing Strategies for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases: From ex vivo to in vivo Strategies.Front Immunol. 2020 May 14;11:674. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00674. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32477325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Promising Therapeutic Effects of Embryonic Stem Cells-Origin Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Experimental Pulmonary Fibrosis Models: Immunomodulatory and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms.Immune Netw. 2023 Dec 11;23(6):e45. doi: 10.4110/in.2023.23.e45. eCollection 2023 Dec. Immune Netw. 2023. PMID: 38188598 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of engineered mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes and their application in autoimmune/inflammatory diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 11;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03295-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37038221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new perspective on therapies involving B-cell depletion in autoimmune diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 May 8;51(1):629. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09575-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38717637
-
Golden Age of Immunotherapy: Challenges and Opportunities.Immune Netw. 2022 Feb 21;22(1):e1. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e1. eCollection 2022 Feb. Immune Netw. 2022. PMID: 35291654 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
IL-17 and IL-21: Their Immunobiology and Therapeutic Potentials.Immune Netw. 2024 Jan 19;24(1):e2. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e2. eCollection 2024 Feb. Immune Netw. 2024. PMID: 38455465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marrack P, Kappler J, Kotzin BL. Autoimmune disease: why and where it occurs. Nat Med. 2001;7:899–905. - PubMed
-
- Cronstein BN, Aune TM. Methotrexate and its mechanisms of action in inflammatory arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Hardy RS, Raza K, Cooper MS. Therapeutic glucocorticoids: mechanisms of actions in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:133–144. - PubMed
-
- Nikiphorou E, Buch MH, Hyrich KL. Biologics registers in RA: methodological aspects, current role and future applications. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13:503–510. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

