Bivalent H1 and H3 COBRA Recombinant Hemagglutinin Vaccines Elicit Seroprotective Antibodies against H1N1 and H3N2 Influenza Viruses from 2009 to 2019
- PMID: 35289635
- PMCID: PMC9006891
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01652-21
Bivalent H1 and H3 COBRA Recombinant Hemagglutinin Vaccines Elicit Seroprotective Antibodies against H1N1 and H3N2 Influenza Viruses from 2009 to 2019
Abstract
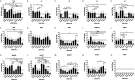
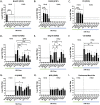
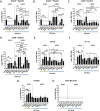
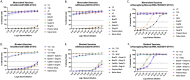
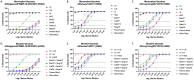
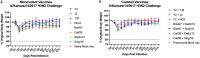
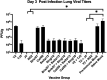
Commercial influenza virus vaccines often elicit strain-specific immune responses and have difficulties preventing illness caused by antigenically drifted viral variants. In the last 20 years, the H3N2 component of the annual vaccine has been updated nearly twice as often as the H1N1 component, and in 2019, a mismatch between the wild-type (WT) H3N2 vaccine strain and circulating H3N2 influenza strains led to a vaccine efficacy of ∼9%. Modern methods of developing computationally optimized broadly reactive antigens (COBRAs) for H3N2 influenza viruses utilize current viral surveillance information to design more broadly reactive vaccine antigens. Here, 7 new recombinant hemagglutinin (rHA) H3 COBRA hemagglutinin (HA) antigens were evaluated in mice. Subsequently, two candidates, J4 and NG2, were selected for further testing in influenza-preimmune animals based on their ability to elicit broadly reactive antibodies against antigenically drifted H3N2 viral isolates. In the preimmune model, monovalent formulations of J4 and NG2 elicited broadly reactive antibodies against recently circulating H3N2 influenza viruses from 2019. Bivalent mixtures of COBRA H1 and H3 rHA, Y2 + J4, and Y2 + NG2 outperformed multiple WT H1+H3 bivalent rHA mixtures by eliciting seroprotective antibodies against H1N1 and H3N2 isolates from 2009 to 2019. Overall, the newly generated COBRA HA antigens, namely, Y2, J4, and NG2, had the ability to induce broadly reactive antibodies in influenza-naive and preimmune animals in both monovalent and bivalent formulations, and these antigens outperformed H1 and H3 WT rHA vaccine antigens by eliciting seroprotective antibodies against panels of antigenically drifted historical H1N1 and H3N2 vaccine strains from 2009 to 2019. IMPORTANCE Standard-of-care influenza virus vaccines are composed of a mixture of antigens from different influenza viral subtypes. For the first time, lead COBRA H1 and H3 HA antigens, formulated as a bivalent vaccine, have been investigated in animals with preexisting immunity to influenza viruses. The cocktail of COBRA HA antigens elicited more broadly reactive anti-HA antibodies than those elicited by a comparator bivalent wild-type HA vaccine against H1 and H3 influenza viruses isolated between 2009 and 2019.
Keywords: COBRA; H1N1; H3N2; bivalent; bivalent vaccine; broadly reactive antibody; cocktail; hemagglutinin; hemagglutinin vaccine; imprinting; influenza; preimmunity; universal influenza.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elicitation of Protective Antibodies against 20 Years of Future H3N2 Cocirculating Influenza Virus Variants in Ferrets Preimmune to Historical H3N2 Influenza Viruses.J Virol. 2019 Jan 17;93(3):e00946-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00946-18. Print 2019 Feb 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30429350 Free PMC article.
-
Computationally Optimized Broadly Reactive Hemagglutinin Elicits Hemagglutination Inhibition Antibodies against a Panel of H3N2 Influenza Virus Cocirculating Variants.J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e01581-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01581-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28978710 Free PMC article.
-
Broadly Reactive H2 Hemagglutinin Vaccines Elicit Cross-Reactive Antibodies in Ferrets Preimmune to Seasonal Influenza A Viruses.mSphere. 2021 Mar 10;6(2):e00052-21. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00052-21. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33692193 Free PMC article.
-
H3N2 influenza viruses in humans: Viral mechanisms, evolution, and evaluation.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018;14(8):1840-1847. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1462639. Epub 2018 May 14. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29641358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broadly neutralizing antibodies to combat influenza virus infection.Antiviral Res. 2024 Jan;221:105785. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105785. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 38145757 Review.
Cited by
-
Bivalent norovirus mRNA vaccine elicits cellular and humoral responses protecting human enteroids from GII.4 infection.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Oct 1;9(1):182. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00976-z. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 39353926 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA vaccines encoding computationally optimized hemagglutinin elicit protective antibodies against future antigenically drifted H1N1 and H3N2 influenza viruses isolated between 2018-2020.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1334670. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1334670. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38533508 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-COBRA hemagglutinin formulated with cGAMP microparticles elicits protective immune responses against influenza viruses.mSphere. 2024 Jul 30;9(7):e0016024. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00160-24. Epub 2024 Jun 26. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38920382 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of an adjuvanted broadly active influenza vaccine in immunocompromised and diverse populations.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Dec 8;9(2):e10634. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10634. eCollection 2024 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38435811 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Pre-Pandemic Trivalent COBRA HA Vaccine in Mice Pre-Immune to Historical H1N1 and H3N2 Influenza Viruses.Viruses. 2023 Jan 11;15(1):203. doi: 10.3390/v15010203. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iuliano AD, Roguski KM, Chang HH, Muscatello DJ, Palekar R, Tempia S, Cohen C, Gran JM, Schanzer D, Cowling BJ, Wu P, Kyncl J, Ang LW, Park M, Redlberger-Fritz M, Yu H, Espenhain L, Krishnan A, Emukule G, van Asten L, Pereira da Silva S, Aungkulanon S, Buchholz U, Widdowson MA, Bresee JS, Global Seasonal Influenza-associated Mortality Collaborator Network. 2018. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: a modelling study. Lancet 391:1285–1300. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33293-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Turner JS, Zhou JQ, Han J, Schmitz AJ, Rizk AA, Alsoussi WB, Lei T, Amor M, McIntire KM, Meade P, Strohmeier S, Brent RI, Richey ST, Haile A, Yang YR, Klebert MK, Suessen T, Teefey S, Presti RM, Krammer F, Kleinstein SH, Ward AB, Ellebedy AH. 2020. Human germinal centres engage memory and naive B cells after influenza vaccination. Nature 586:127–132. 10.1038/s41586-020-2711-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

