Plasmalogens Eliminate Aging-Associated Synaptic Defects and Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Mice
- PMID: 35281262
- PMCID: PMC8906368
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.815320
Plasmalogens Eliminate Aging-Associated Synaptic Defects and Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Mice
Abstract
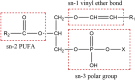
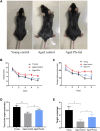
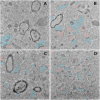
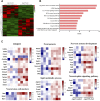
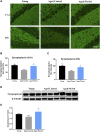
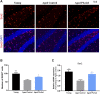
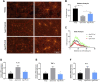
Neurodegeneration is a pathological condition in which nervous system or neuron losses its structure, function, or both leading to progressive neural degeneration. Growing evidence strongly suggests that reduction of plasmalogens (Pls), one of the key brain lipids, might be associated with multiple neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Plasmalogens are abundant members of ether-phospholipids. Approximately 1 in 5 phospholipids are plasmalogens in human tissue where they are particularly enriched in brain, heart and immune cells. In this study, we employed a scheme of 2-months Pls intragastric administration to aged female C57BL/6J mice, starting at the age of 16 months old. Noticeably, the aged Pls-fed mice exhibited a better cognitive performance, thicker and glossier body hair in appearance than that of aged control mice. The transmission electron microscopic (TEM) data showed that 2-months Pls supplementations surprisingly alleviate age-associated hippocampal synaptic loss and also promote synaptogenesis and synaptic vesicles formation in aged murine brain. Further RNA-sequencing, immunoblotting and immunofluorescence analyses confirmed that plasmalogens remarkably enhanced both the synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis in aged murine hippocampus. In addition, we have demonstrated that Pls treatment inhibited the age-related microglia activation and attenuated the neuroinflammation in the murine brain. These findings suggest for the first time that Pls administration might be a potential intervention strategy for halting neurodegeneration and promoting neuroregeneration.
Keywords: aging; microglia; neurogenesis; neuroinflammation; plasmalogen; synaptogenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Gu, Chen, Sun, Wang, Wang, Lin, Lei, Zhang, Lv, Jiang, Deng, Collman and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of Ether-Type Glycerophospholipids, Plasmalogens, by NF-κB Signal Leading to Microglial Activation.J Neurosci. 2017 Apr 12;37(15):4074-4092. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3941-15.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28292831 Free PMC article.
-
Oral ingestion of plasmalogens can attenuate the LPS-induced memory loss and microglial activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Feb 19;496(4):1033-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.078. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29337053
-
Biological Functions of Plasmalogens.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1299:171-193. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-60204-8_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33417215 Review.
-
Plasmalogens Inhibit Endocytosis of Toll-like Receptor 4 to Attenuate the Inflammatory Signal in Microglial Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 May;56(5):3404-3419. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1307-2. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30128650
-
Plasmalogens inhibit neuroinflammation and promote cognitive function.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Jan;192:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.11.005. Epub 2022 Nov 5. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 36347405 Review.
Cited by
-
Role and Function of Peroxisomes in Neuroinflammation.Cells. 2024 Oct 5;13(19):1655. doi: 10.3390/cells13191655. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Strategies to Reduce the SARS-CoV-2 Amyloid Deposition in the Brain and Prevent COVID-19-Exacerbated Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 16;17(6):788. doi: 10.3390/ph17060788. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid biology of plasmalogen-derived halolipids: Signature molecules of myeloperoxidase and eosinophil peroxidase activity.Redox Biochem Chem. 2023 Dec;5-6:100011. doi: 10.1016/j.rbc.2023.100011. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Redox Biochem Chem. 2023. PMID: 38073668 Free PMC article.
-
Orally Administered Plasmalogens Alleviate Negative Mood States and Enhance Mental Concentration: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 2;10:894734. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.894734. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35721497 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Plasmalogens: A Gift from the Sea with Benefits for Age-Associated Diseases.Molecules. 2023 Aug 29;28(17):6328. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176328. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angelova A., Angelov B., Drechsler M., Bizien T., Gorshkova Y. E., Deng Y. (2021). Plasmalogen-Based Liquid Crystalline Multiphase Structures Involving Docosapentaenoyl Derivatives Inspired by Biological Cubic Membranes. Front. Cel. Dev. Biol. 9, 617984. 10.3389/fcell.2021.617984 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

