A Paradoxical Effect of Interleukin-32 Isoforms on Cancer
- PMID: 35281008
- PMCID: PMC8913503
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.837590
A Paradoxical Effect of Interleukin-32 Isoforms on Cancer
Abstract
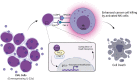
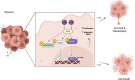
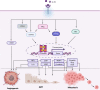
IL-32 plays a contradictory role such as tumor proliferation or suppressor in cancer development depending on the cancer type. In most cancers, it was found that the high expression of IL-32 was associated with more proliferative and progression of cancer. However, studying the isoforms of IL-32 cytokine has placed its paradoxical role into a wide range of functions based on its dominant isoform and surrounding environment. IL-32β, for example, was found mostly in different types of cancer and associated with cancer expansion. This observation is legitimate since cancer exhibits some hypoxic environment and IL-32β was known to be induced under hypoxic conditions. However, IL-32θ interacts directly with protein kinase C-δ reducing NF-κB and STAT3 levels to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This effect could explain the different functions of IL-32 isoforms in cancer. However, pro- or antitumor activity which is dependant on obesity, gender, and age as it relates to IL-32 has yet to be studied. Obesity-related IL-32 regulation indicated the role of IL-32 in cancer metabolism and inflammation. IL-32-specific direction in cancer therapy is difficult to conclude. In this review, we address that the paradoxical effect of IL-32 on cancer is attributed to the dominant isoform, cancer type, tumor microenvironment, and genetic background. IL-32 seems to have a contradictory role in cancer. However, investigating multiple IL-32 isoforms could explain this doubt and bring us closer to using them in therapy.
Keywords: hypoxia; interleukin-32; metastasis; stromal tumor; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Shim, Lee, Hisham, Kim, Nguyen, Taitt, Hwang, Jhun, Park, Lee, Yeom, Kim, Kim and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulatory effects of point-mutated IL-32θ (A94V) on tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Biofactors. 2024 Mar-Apr;50(2):294-310. doi: 10.1002/biof.2005. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Biofactors. 2024. PMID: 37658685
-
Interleukin-32β stimulates migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7cells via the VEGF-STAT3 signaling pathway.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2013 Dec;36(6):493-503. doi: 10.1007/s13402-013-0154-4. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 24114327
-
Antitumor activity of IL-32β through the activation of lymphocytes, and the inactivation of NF-κB and STAT3 signals.Cell Death Dis. 2013 May 23;4(5):e640. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.166. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23703385 Free PMC article.
-
IL-32θ: a recently identified anti-inflammatory variant of IL-32 and its preventive role in various disorders and tumor suppressor activity.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Nov 15;9(11):4726-4737. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 29218075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the role of IL-32 in cancer.Semin Immunol. 2018 Aug;38:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 May 8. Semin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29747940 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-32 as a biomarker in rheumatic diseases: A narrative review.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1140373. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1140373. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human IL-32θA94V mutant attenuates monocyte-endothelial adhesion by suppressing the expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 via binding to cell surface receptor integrin αVβ3 and αVβ6 in TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs.Front Immunol. 2023 May 9;14:1160301. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1160301. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37228610 Free PMC article.
-
IL-32/NFκB/miR-205 loop sustains the high expression of IL-32 and enhances the motility of cervical cancer cells.Hum Cell. 2024 Sep;37(5):1434-1445. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01094-7. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38902566
-
Single-cell long-read targeted sequencing reveals transcriptional variation in ovarian cancer.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 12;15(1):6916. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51252-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39134520 Free PMC article.
-
IL-2 and TCR stimulation induce expression and secretion of IL-32β by human T cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 15;15:1437224. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437224. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39211051 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

