Phosphoinositide 3 Kinase γ Plays a Critical Role in Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 35269396
- PMCID: PMC8909888
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11050772
Phosphoinositide 3 Kinase γ Plays a Critical Role in Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
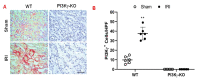
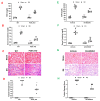
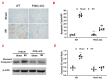
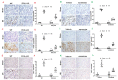
Inflammatory cells contribute to the pathogenesis of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). However, the signaling mechanisms underlying the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the kidney are not well understood. In this study, we examined the effects of phosphoinositide 3 kinase γ (PI3Kγ) on inflammatory cells infiltration into the kidney in response to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Compared with wild-type mice, PI3Kγ knockout mice displayed less IRI in the kidney with fewer tubular apoptotic cell. Furthermore, PI3Kγ deficiency decreased the number of infiltrated neutrophils, macrophages, and T cells in the kidney, which was accompanied by a decrease in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the kidney. Moreover, wild-type mice treated with AS-605240, a selective PI3Kγ inhibitor, displayed less tubular damage, accumulated fewer inflammatory cells, and expressed less proinflammatory molecules in the kidney following IRI. These results demonstrate that PI3Kγ has a critical role in the pathogenesis of kidney damage in IRI, indicating that PI3Kγ inhibition may serve as a potential therapeutic strategy for the prevention of ischemia-reperfusion-induced kidney injury.
Keywords: PI3Kγ; acute kidney injury; inflammation; ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ deficiency attenuates kidney injury and fibrosis in angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020 Sep 1;35(9):1491-1500. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa062. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32500132 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma plays a central role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute experimental stroke.Stroke. 2011 Jul;42(7):2033-44. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.601369. Epub 2011 May 5. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21546487 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL16/ROCK1 signaling pathway exacerbates acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Feb;98:347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.063. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29275176
-
The role of PI3Kγ in the immune system: new insights and translational implications.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Nov;22(11):687-700. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00701-8. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35322259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designing Small Molecule PI3Kγ Inhibitors: A Review of Structure-Based Methods and Computational Approaches.J Med Chem. 2024 Jul 11;67(13):10530-10547. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00347. Epub 2024 Jun 19. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38988222 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-Term Preconditioning with Insulin and Glucose Efficiently Protected the Kidney Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via the P-AKT-Bax-Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway in Mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jun 20;18:2461-2474. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S465836. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38915866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao M., Wang Y., Li L., Liu S., Wang C., Yuan Y., Yang G., Chen Y., Cheng J., Lu Y., et al. Mitochondrial ROS promote mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in ischemic acute kidney injury by disrupting TFAM-mediated mtDNA maintenance. Theranostics. 2021;11:1845–1863. doi: 10.7150/thno.50905. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

