The Effect of Surface Substrate Treatments on the Bonding Strength of Aluminium Inserts with Glass-Reinforced Poly(phenylene) Sulphide
- PMID: 35269158
- PMCID: PMC8911945
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15051929
The Effect of Surface Substrate Treatments on the Bonding Strength of Aluminium Inserts with Glass-Reinforced Poly(phenylene) Sulphide
Abstract
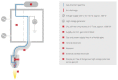
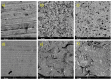
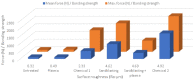
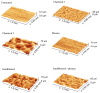
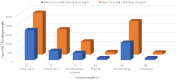
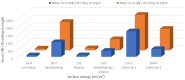
Materials composed of a polymer matrix reinforced with carbon/glass fibres providing lightweight and superior mechanical properties are widely used as structural components for automotive and aerospace applications. However, such parts need to be joined with various metal alloys to obtain better mechanical performance in many structural elements. Many studies have reported enhancements in polymer-metal bonding using adhesives, adhesive/rivet combined joints, and different surface treatments. This study investigated the influences of various surface treatments on the adhesion between glass-reinforced poly(phenylene) sulphide (PPS) and aluminium alloy during the injection over-moulding process. Adhesion strength was evaluated via the shear test. Correlations for the shear strength of the polymer-metal with different metal-substrate treatments were studied. Since the strongest bonding was attained in the treatment with the highest roughness, this value, as it determines the level of micromechanical interlocking of connected materials, seems to be a critical factor affecting the adhesion strength. Three-dimensional (3D) topographic images characterized with a 3D optical microscope indicated that there was a meaningful influence exerted by the interface topologies of the aluminium substrates used for the over-moulding process. The results further indicated that increases in a substrate's surface energy in connection with atmospheric plasma treatments negatively influence the final level of the bonding mechanism.
Keywords: PPS–aluminium bi-component; polymer–metal bonding; surface modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surface Treatments' Influence on the Interfacial Bonding between Glass Fibre Reinforced Elium® Composite and Polybutylene Terephthalate.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jul 3;17(13):3276. doi: 10.3390/ma17133276. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998358 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on Adhesive Bonding of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Jan 15;11(1):139. doi: 10.3390/polym11010139. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30960123 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Coupling Agents on Interfacial Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Aluminum Laminates.Materials (Basel). 2021 Feb 21;14(4):1019. doi: 10.3390/ma14041019. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670036 Free PMC article.
-
Surface modification of glass fiber-reinforced composite posts to enhance their bond strength to resin-matrix cements: an integrative review.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Jan;26(1):95-107. doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-04221-y. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 34713360 Review.
-
3D Printing of Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites Using Fused Deposition Modeling: A Status Review.Materials (Basel). 2021 Aug 12;14(16):4520. doi: 10.3390/ma14164520. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34443044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Surface Treatments' Influence on the Interfacial Bonding between Glass Fibre Reinforced Elium® Composite and Polybutylene Terephthalate.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jul 3;17(13):3276. doi: 10.3390/ma17133276. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998358 Free PMC article.
-
Wettability and Surface Roughness Analysis of Laser Surface Texturing of AISI 430 Stainless Steel.Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;15(8):2955. doi: 10.3390/ma15082955. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li X., Liu F., Gong N., Yang C., Wang B. Surface Topography Induced High Injection Joining Strength of Polymer-Metal Composite and Fracture Mechanism. Compos. Struct. 2018;184:545–553. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.10.020. - DOI
-
- Martinsen K., Hu S.J., Carlson B.E. Joining of Dissimilar Materials. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2015;64:679–699. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2015.05.006. - DOI
-
- Mandolfino C., Lertora E., Gambaro C. Key Engineering Materials. Volume 554–557. Trans Tech Publications Ltd.; Bach, Switzerland: 2013. Effect of Surface Pretreatment on the Performance of Adhesive-Bonded Joints; pp. 996–1006.
-
- Xu Z., Li N. Effects of Surface Microstructure and Molding Parameters on Injection Bonding Strength of Polyphenylenesulphide-Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Express. 2020;10:640–647. doi: 10.1166/mex.2020.1688. - DOI
-
- Iqbal H.M.S., Bhowmik S., Poulis J.A., Benedictus R. Effect of Plasma Treatment and Electron Beam Radiations on the Strength of Nanofilled Adhesive-Bonded Joints. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010;50:1505–1511. doi: 10.1002/pen.21628. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

