Silencing of A-kinase anchor protein 4 inhibits the metastasis and growth of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35253625
- PMCID: PMC8974088
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1977105
Silencing of A-kinase anchor protein 4 inhibits the metastasis and growth of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
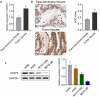
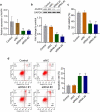
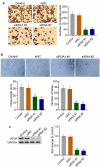
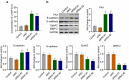
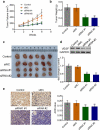
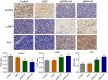
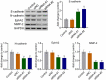
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the most malignant tumors. The treatment of advanced NSCLC can be challenging due to drug resistance. The discovery of novel cancer-testis antigens to develop new strategies for advanced metastatic NSCLC is required. AKAP4 is an oncogene discovered in some malignant tumors, and its molecular function of AKAP4 in NSCLC is unknown. This study aimed to explore the potential function of AKAP4 in the development and progression of NSCLC. AKAP-4 was found to be significantly upregulated in both clinical NSCLC tissues and NSCLC cell lines. Cell viability and migration were suppressed, apoptosis was induced, and tube formation was inhibited by the knockdown of AKAP-4, accompanied by the downregulation of VEGF, N-cadherin, EphA2, and MMP-2, and upregulation of c-AMP, PKA, and E-cadherin. In vivo xenograft experiments revealed that tumor growth was inhibited by the knockdown of AKAP4, accompanied by the activation of c-AMP/PKA signaling and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression. Our results show that AKAP4 might be an important target for treating NSCLC because of its function in promoting the migration and proliferation of NSCLC cells.
Keywords: AKAP4; PKA; migration; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of A-Kinase Anchor Protein 4 (AKAP4) Inhibits Proliferation and Progression of Thyroid Cancer.Oncol Res. 2017 Jul 5;25(6):873-878. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14783701102564. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 27983916 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing of A-kinase anchor protein 4 inhibits cervical cancer growth in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Gene Ther. 2013 Jul;20(7):413-20. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2013.32. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23764900
-
Knockdown of TRIM66 inhibits malignant behavior and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Aug;214(8):1130-1135. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.06.008. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 29929749
-
Knockdown of A-kinase anchor protein 4 inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human gastric cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Dec;119(12):10013-10020. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27331. Epub 2018 Aug 26. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30145836
-
Novel antigens in non-small cell lung cancer: SP17, AKAP4, and PTTG1 are potential immunotherapeutic targets.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 20;6(5):2812-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2802. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25739119 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IQ Motif Containing GTPase Activating Proteins (IQGAPs), A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs) and Kinase Suppressor of Ras Proteins (KSRs) in Scaffolding Oncogenic Pathways and Their Therapeutic Potential.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 6;7(50):45837-45848. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05505. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis identifies AKAP8L as an immunological and prognostic biomarker of pan-cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Sep 7;15(17):8851-8872. doi: 10.18632/aging.205003. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37683130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C.. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–454. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
