Cell-Free DNA Variables including Gene Mutations in CA15-3 Normal Breast Cancer Reflect Prognosis
- PMID: 35251373
- PMCID: PMC8894049
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5470166
Cell-Free DNA Variables including Gene Mutations in CA15-3 Normal Breast Cancer Reflect Prognosis
Abstract
Background: Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has attracted considerable attention in precision medicine. However, few data are available regarding to the prognostic value of cfDNA variables in CA15-3 normal breast cancer (BC) patients. Here, we aimed at investigating the prognostic value of cfDNA variables including gene mutations in CA15-3 normal BC patients.
Methods: A total of 68 BC patients with normal CA15-3 levels were enrolled. cfDNA concentration and integrity were assessed based on qPCR. cfDNA gene mutations were conducted by using next gene sequencing (NGS). The association between cfDNA variables and the prognosis of patients was analyzed.
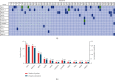
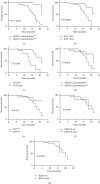
Results: cfDNA concentration was related to tumor stage (P = 0.002), metastases (P = 0.001), and distant metastases (P < 0.001). The elevated copy number variants (CNV) were found in distant metastasis patients compared with patients without distant metastases (P = 0.008). Nineteen mutant genes were validated in enrolled CA15-3 normal BC patients. Thirty-two patients (47.0%) had single nucleotide variants (SNV), and 13 (19.1%) patients had TP53 mutations (TP53 mut). SNV (P = 0.033) was related to tumor stage, and TP53 mut was related to metastases (P = 0.016) and distant metastases (P = 0.006). In multivariate logistic analysis, cfDNA concentration was associated with metastases (OR = 3.404, 95% CI: 1.074-10.788, P = 0.037) and distant metastases (OR = 13.750, 95% CI: 1.473-128.358, P = 0.021). Cases with high cfDNA levels (>15.6 ng/ml), SNV, and TP53 mut showed worse DFS compared with patients with low cfDNA levels (P < 0.001), without SNV (P = 0.002) and with TP53 wildtype (P < 0.001), respectively. In the multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, cfDNA concentration was an independent predictor of poor survival (HR = 5.786, 95% CI: 1.101-30.407, P = 0.038).
Conclusions: Assessment of cfDNA concentration, CNV, SNV, and TP53 mut could be useful in predicting prognosis for CA15-3 normal BC patients. The cfDNA concentration was an independent predictor prognostic factor in CA15-3 normal BC patients.
Copyright © 2022 Juan Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of analysis of cfDNA for detection of single nucleotide variants and copy number variants in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2019 May 17;19(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5698-x. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31101027 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma cell-free DNA chromosomal instability analysis by low-pass whole-genome sequencing to monitor breast cancer relapse.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Nov;178(1):63-73. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05375-w. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31364001
-
Plasma ALU-247, ALU-115, and cfDNA Integrity as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;187(3):1028-1045. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2858-4. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30151636
-
Liquid biopsy prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis, cancer recurrence, and patient survival in breast cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Oct;97(42):e12862. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012862. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30334995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of circulating cell-free DNA in the survival of breast cancer patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(28):e11417. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011417. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29995790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perey L., Hayes D. F., Maimonis P., Abe M., O'Hara C., Kufe D. W. Tumor selective reactivity of a monoclonal antibody prepared against a recombinant peptide derived from the DF3 human breast carcinoma-associated antigen. Cancer Research . 1992;52(9):2563–2568. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

