An Epigenetic Alphabet of Crop Adaptation to Climate Change
- PMID: 35251130
- PMCID: PMC8888914
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.818727
An Epigenetic Alphabet of Crop Adaptation to Climate Change
Abstract
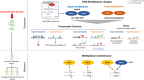
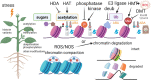
Crop adaptation to climate change is in a part attributed to epigenetic mechanisms which are related to response to abiotic and biotic stresses. Although recent studies increased our knowledge on the nature of these mechanisms, epigenetics remains under-investigated and still poorly understood in many, especially non-model, plants, Epigenetic modifications are traditionally divided into two main groups, DNA methylation and histone modifications that lead to chromatin remodeling and the regulation of genome functioning. In this review, we outline the most recent and interesting findings on crop epigenetic responses to the environmental cues that are most relevant to climate change. In addition, we discuss a speculative point of view, in which we try to decipher the "epigenetic alphabet" that underlies crop adaptation mechanisms to climate change. The understanding of these mechanisms will pave the way to new strategies to design and implement the next generation of cultivars with a broad range of tolerance/resistance to stresses as well as balanced agronomic traits, with a limited loss of (epi)genetic variability.
Keywords: abiotic stresses; adaptation; climate change; environmental stresses; epigenetic code; epigenetics.
Copyright © 2022 Guarino, Cicatelli, Castiglione, Agius, Orhun, Fragkostefanakis, Leclercq, Dobránszki, Kaiserli, Lieberman-Lazarovich, Sõmera, Sarmiento, Vettori, Paffetti, Poma, Moschou, Gašparović, Yousefi, Vergata, Berger, Gallusci, Miladinović and Martinelli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deciphering the Epigenetic Alphabet Involved in Transgenerational Stress Memory in Crops.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7118. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137118. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant epigenomics for extenuation of abiotic stresses: challenges and future perspectives.J Exp Bot. 2021 Oct 26;72(20):6836-6855. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab337. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 34302734 Review.
-
Epigenetics: possible applications in climate-smart crop breeding.J Exp Bot. 2020 Aug 17;71(17):5223-5236. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa188. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32279074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and epigenomics: underlying mechanisms, relevance, and implications in crop improvement.Funct Integr Genomics. 2020 Nov;20(6):739-761. doi: 10.1007/s10142-020-00756-7. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Funct Integr Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33089419 Review.
-
In Response to Abiotic Stress, DNA Methylation Confers EpiGenetic Changes in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 30;10(6):1096. doi: 10.3390/plants10061096. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070712 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic variation: A major player in facilitating plant fitness under changing environmental conditions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 18;10:1020958. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1020958. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36340045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vegetal memory through the lens of transcriptomic changes - recent progress and future practical prospects for exploiting plant transcriptional memory.Plant Signal Behav. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2383515. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2024.2383515. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Plant Signal Behav. 2024. PMID: 39077764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Translational Modifications in Histones and Their Role in Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants.Proteomes. 2023 Nov 22;11(4):38. doi: 10.3390/proteomes11040038. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 38133152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Improving abiotic stress tolerance of forage grasses - prospects of using genome editing.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 7;14:1127532. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1127532. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36824201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad F., Farman K., Waseem M., Rana R. M., Nawaz M. A., Rehman H. M., et al. (2019). Genome-wide Identification, Classification, Expression Profiling and DNA Methylation (5mC) Analysis of Stress-Responsive ZFP Transcription Factors in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Gene 718, 144018. 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144018 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altieri M. A., Nicholls C. I., Henao A., Lana M. A. (2015). Agroecology and the Design of Climate Change-Resilient Farming Systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35 (3), 869–890. 10.1007/s13593-015-0285-2 - DOI
-
- Annunziato A. (2008). DNA Packaging: Nucleosomes and Chromatin. Nat. Educat 1 (1), 26.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

