Diacerein counteracts acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via targeting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-4/MCP-1 signaling pathways
- PMID: 35244883
- PMCID: PMC8967791
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-022-01373-7
Diacerein counteracts acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via targeting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-4/MCP-1 signaling pathways
Abstract
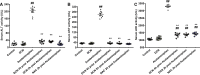
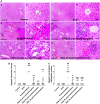
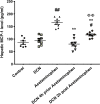
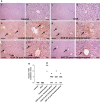
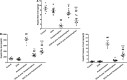
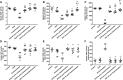
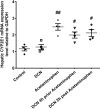
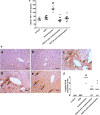
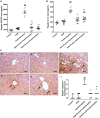
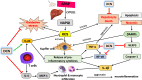
The current study aims at repurposing the anti-arthritic drug diacerein (DCN) for the treatment of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and investigating the potential underlying mechanisms. Mice were randomly divided into six groups receiving either no treatment (control group), 20 mg/kg DCN i.p, 400 mg/kg acetaminophen i.p, DCN 4 h before acetaminophen, DCN 2 h after acetaminophen, or 400 mg/kg N-acetylcysteine (NAC) i.p, 2 h after acetaminophen. Biomarkers of liver dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis were assessed. Hepatic necroinflammatory changes were evaluated along with hepatic expression of NF-κB and caspase-1. The levels of NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-4, MCP-1, and TNF-α in the liver, as well as CYP2E1 mRNA expression, were measured. Diacerein significantly reduced biomarkers of liver dysfunction, oxidative stress, hepatocyte necrosis, and infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages whether administered 4 h before or 2 h after acetaminophen. Further, the effects were comparable to those of NAC. Diacerein also counteracted acetaminophen-induced hepatocellular apoptosis by increasing Bcl-2 and decreasing Bax and caspase-3 expression levels. Moreover, DCN normalized hepatic TNF-α and significantly decreased NF-κB p65 expression. Accordingly, DCN can prevent or reverse acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice, suggesting potential utility as a repurposed drug for clinical treatment.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; Diacerein; IL-1β; IL-4; MCP-1; NLRP3.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of allicin against acetaminophen-induced liver injury: Role of inflammasome pathway, apoptosis, and liver regeneration.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020 May;34(5):e22470. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22470. Epub 2020 Feb 10. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32040233
-
Distinct roles of NF-kappaB p50 in the regulation of acetaminophen-induced inflammatory mediator production and hepatotoxicity.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 1;211(2):157-65. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.06.024. Epub 2005 Aug 2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16081117
-
Diacerein Downregulates NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-6/STAT3 Pathways of Inflammation and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cadmium Testicular Toxicity.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Jun;195(2):499-505. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01865-6. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31401744
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Improved protective effects of American ginseng berry against acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity through TNF-α-mediated caspase-3/-8/-9 signaling pathways.Phytomedicine. 2018 Dec 1;51:128-138. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.234. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466610
Cited by
-
Kaempferol sophoroside glucoside mitigates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: Role of Nrf2/NF-κB and JNK/ASK-1 signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 May 17;10(10):e31448. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31448. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38813141 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2 regulates autophagy to mitigate oxidative stress in aged mice with acute liver injury.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Mar 1;10(1):107. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01870-2. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38429284 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Programmed Cell Death in Acute Liver Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3067. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043067. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissection of cellular and molecular mechanisms of aristolochic acid-induced hepatotoxicity via single-cell transcriptomics.Precis Clin Med. 2022 Sep 22;5(4):pbac023. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbac023. eCollection 2022 Dec. Precis Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36349141 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome in Acute and Chronic Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 20;25(8):4537. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084537. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

