The functional mechanism of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of animal models with Alzheimer's disease: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis
- PMID: 35241159
- PMCID: PMC8895531
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02765-8
The functional mechanism of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of animal models with Alzheimer's disease: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis
Abstract
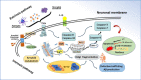
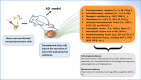
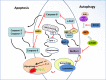
The transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs) alleviates neuropathology and improves cognitive deficits in animal models with Alzheimer's disease. However, the underlying mechanism remains undefined. Based on meta-analysis and comprehensive review, high-profile studies support the theory that transplanted BMMSCs activate autophagy, as evidenced by the expression levels of signal molecules such as Beclin-1, Atg5, LC3-II, and mTOR. Functional autophagy mitigates neuronal apoptosis, which is reflected by the alterations of IAPs, Bcl-2, caspase-3, and so forth. Moreover, the transplantation of BMMSCs can decrease aberrant amyloid-beta peptides as well as tau aggregates, inhibit neuroinflammation, and stimulate synaptogenesis. There is a signal crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis, which may be regulated to produce synergistic effect on the preconditioning of stem cells. Forasmuch, the therapeutic effect of transplanted BMMSCs can be enhanced by autophagy and/or apoptosis modulators.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Apoptosis; Autophagy; Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves cognitive deficits and alleviates neuropathology in animal models of Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analytic review on potential mechanisms.Transl Neurodegener. 2020 May 27;9(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00199-x. Transl Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 32460886 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Mechanism of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Animal Models with Alzheimer's Disease: Inhibition of Neuroinflammation.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Sep 17;14:4761-4775. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S327538. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34566422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes derived from MSC pre-treated with oridonin alleviates myocardial IR injury by suppressing apoptosis via regulating autophagy activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(12):5486-5496. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16558. Epub 2021 May 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33955654 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Balance Mechanism Participates in Stem Cell Therapy to Alleviate Neuropathology and Cognitive Impairment in Animal Models with Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2021 Oct 15;10(10):2757. doi: 10.3390/cells10102757. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Applications in Alzheimer's Disease.Glob Med Genet. 2023 Dec 11;10(4):382-387. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1777087. eCollection 2023 Dec. Glob Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 38089680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and γ-Secretase Inhibitor Treatments Suppress Amyloid-β25-35-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Rat Dams and Cortical Degeneration in Offspring.Stem Cells Int. 2023 May 25;2023:2690949. doi: 10.1155/2023/2690949. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 37274020 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Begacestat Mitigate Amyloid-β 25-35-Induced Cognitive Decline in Rat Dams and Hippocampal Deteriorations in Offspring.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;12(7):905. doi: 10.3390/biology12070905. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508337 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients in the presence of autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Sep 15;15(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03820-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39278909 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Targeting Necroptosis: A Novel Therapeutic Option for Retinal Degenerative Diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;19(2):658-674. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.77994. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36632450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(4):329–344. - PubMed
-
- Pierzynowska K, Podlacha M, Gaffke L, Majkutewicz I, Mantej J, Wegrzyn A, et al. Autophagy-dependent mechanism of genistein-mediated elimination of behavioral and biochemical defects in the rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 2019;148:332–346. - PubMed
-
- Qin C, Lu Y, Wang K, Bai L, Shi G, Huang Y, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves cognitive deficits and alleviates neuropathology in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analytic review on potential mechanisms. Transl Neurodegener. 2020;9(1):20. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

