Site-Specific Protein Ubiquitylation Using an Engineered, Chimeric E1 Activating Enzyme and E2 SUMO Conjugating Enzyme Ubc9
- PMID: 35237717
- PMCID: PMC8883482
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c01490
Site-Specific Protein Ubiquitylation Using an Engineered, Chimeric E1 Activating Enzyme and E2 SUMO Conjugating Enzyme Ubc9
Abstract
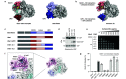
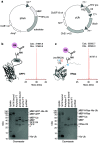
Ubiquitylation-the attachment of ubiquitin (Ub) to proteins in eukaryotic cells-involves a vast number of enzymes from three different classes, resulting in heterogeneous attachment sites and ubiquitin chains. Recently, we introduced lysine acylation using conjugating enzymes (LACE) in which ubiquitin or peptide thioester is site-specifically transferred to a short peptide tag by the SUMO E2 conjugating enzyme Ubc9. This process, however, suffers from slow kinetics-due to a rate-limiting thioester loading step-and the requirement for thioesters restricts its use to in vitro reactions. To overcome these challenges, we devised a chimeric E1 containing the Ub fold domain of the SUMO E1 and the remaining domains of the Ub E1, which activates and loads native Ub onto Ubc9 and obviates the need for Ub thioester in LACE. The chimeric E1 was subjected to directed evolution to improve its apparent second-order rate constant (k cat/K M) 400-fold. We demonstrate the utility of the chimeric E1 by site-specific transfer of mono- and oligo-Ub to various target proteins in vitro. Additionally, the chimeric E1, Ubc9, Ub, and the target protein can be coexpressed in Escherichia coli for the facile preparation of monoubiquitylated proteins.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of a ubiquitin E1-E2 complex: insights to E1-E2 thioester transfer.Mol Cell. 2013 Mar 7;49(5):884-96. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.013. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23416107 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine acylation using conjugating enzymes for site-specific modification and ubiquitination of recombinant proteins.Nat Chem. 2020 Nov;12(11):1008-1015. doi: 10.1038/s41557-020-0528-y. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Nat Chem. 2020. PMID: 32929246
-
Domain alternation and active site remodeling are conserved structural features of ubiquitin E1.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 21;292(29):12089-12099. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.787622. Epub 2017 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28572513 Free PMC article.
-
The family of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s): deciding between life and death of proteins.FASEB J. 2010 Apr;24(4):981-93. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-136259. Epub 2009 Nov 25. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 19940261 Review.
-
RING-Between-RING E3 Ligases: Emerging Themes amid the Variations.J Mol Biol. 2017 Nov 10;429(22):3363-3375. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.08.008. Epub 2017 Aug 19. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28827147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Site-Specific Protein Labeling and Generation of Defined Ubiquitin-Protein Conjugates Using an Asparaginyl Endopeptidase.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Jul 27;144(29):13118-13126. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c02191. Epub 2022 Jul 18. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35850488 Free PMC article.
-
Nature-inspired protein ligation and its applications.Nat Rev Chem. 2023 Apr;7(4):234-255. doi: 10.1038/s41570-023-00468-z. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Nat Rev Chem. 2023. PMID: 37117416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-guided engineering enables E3 ligase-free and versatile protein ubiquitination via UBE2E1.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 10;15(1):1266. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45635-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38341401 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Assembly Modification of Protein Cages by Ubc9-Mediated Lysine Acylation.Chembiochem. 2022 Oct 19;23(20):e202200332. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202200332. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35951442 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting NEDD8-activating enzyme for cancer therapy: developments, clinical trials, challenges and future research directions.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jul 31;16(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01485-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37525282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

