Transport, functions, and interaction of calcium and manganese in plant organellar compartments
- PMID: 35235665
- PMCID: PMC8890496
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiab122
Transport, functions, and interaction of calcium and manganese in plant organellar compartments
Abstract
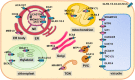
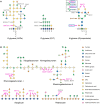
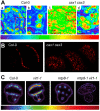
Calcium (Ca2+) and manganese (Mn2+) are essential elements for plants and have similar ionic radii and binding coordination. They are assigned specific functions within organelles, but share many transport mechanisms to cross organellar membranes. Despite their points of interaction, those elements are usually investigated and reviewed separately. This review takes them out of this isolation. It highlights our current mechanistic understanding and points to open questions of their functions, their transport, and their interplay in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), vesicular compartments (Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network, pre-vacuolar compartment), vacuoles, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and peroxisomes. Complex processes demanding these cations, such as Mn2+-dependent glycosylation or systemic Ca2+ signaling, are covered in some detail if they have not been reviewed recently or if recent findings add to current models. The function of Ca2+ as signaling agent released from organelles into the cytosol and within the organelles themselves is a recurrent theme of this review, again keeping the interference by Mn2+ in mind. The involvement of organellar channels [e.g. glutamate receptor-likes (GLR), cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (CNGC), mitochondrial conductivity units (MCU), and two-pore channel1 (TPC1)], transporters (e.g. natural resistance-associated macrophage proteins (NRAMP), Ca2+ exchangers (CAX), metal tolerance proteins (MTP), and bivalent cation transporters (BICAT)], and pumps [autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPases (ACA) and ER Ca2+-ATPases (ECA)] in the import and export of organellar Ca2+ and Mn2+ is scrutinized, whereby current controversial issues are pointed out. Mechanisms in animals and yeast are taken into account where they may provide a blueprint for processes in plants, in particular, with respect to tunable molecular mechanisms of Ca2+ versus Mn2+ selectivity.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The medial-Golgi ion pump Pmr1 supplies the yeast secretory pathway with Ca2+ and Mn2+ required for glycosylation, sorting, and endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 May;9(5):1149-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.5.1149. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9571246 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and distribution of organelles and cellular location of calcium transporters in Neurospora crassa.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Dec;8(12):1845-55. doi: 10.1128/EC.00174-09. Epub 2009 Oct 2. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19801418 Free PMC article.
-
The trans-Golgi-localized protein BICAT3 regulates manganese allocation and matrix polysaccharide biosynthesis.Plant Physiol. 2022 Nov 28;190(4):2579-2600. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac387. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35993897 Free PMC article.
-
The Ca2+/Mn2+ pumps in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Dec 6;1742(1-3):103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.08.018. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15590060 Review.
-
Vacuolar degradation of plant organelles.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 3;36(9):3036-3056. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae128. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38657116 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA editing events and expression profiles of mitochondrial protein-coding genes in the endemic and endangered medicinal plant, Corydalis saxicola.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 6;15:1332460. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1332460. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38379941 Free PMC article.
-
An Arabidopsis mutant line lacking the mitochondrial calcium transport regulator MICU shows an altered metabolite profile.Plant Signal Behav. 2023 Dec 31;18(1):2271799. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2023.2271799. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Plant Signal Behav. 2023. PMID: 37879964 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of stress-induced calcium signals in the crop species barley and the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Sep 17;22(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03820-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36114461 Free PMC article.
-
CamelliA-based simultaneous imaging of Ca2+ dynamics in subcellular compartments.Plant Physiol. 2022 Mar 28;188(4):2253-2271. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac020. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35218352 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating membrane transport, signaling, and physiology.Plant Physiol. 2022 Feb 4;188(2):921-923. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab585. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34908141 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alejandro S, Cailliatte R, Alcon C, Dirick L, Domergue F, Correia D, Castaings L, Briat J-F, Mari S, Curie C (2017) Intracellular distribution of manganese by the trans-Golgi network transporter NRAMP2 is critical for photosynthesis and cellular redox homeostasis. Plant Cell 29:3068–3084 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

