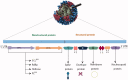
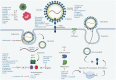
The vital role of animal, marine, and microbial natural products against COVID-19
- PMID: 35234563
- PMCID: PMC8896193
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2039215
The vital role of animal, marine, and microbial natural products against COVID-19
Abstract
Context: Since the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2, researchers have been working on finding ways to prevent viral entry and pathogenesis. Drug development from naturally-sourced pharmacological constituents may be a fruitful approach to COVID-19 therapy.
Objective: Most of the published literature has focussed on medicinal plants, while less attention has been given to biodiverse sources such as animal, marine, and microbial products. This review focuses on highlighting natural products and their derivatives that have been evaluated for antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties.
Methods: We searched electronic databases such as PubMed, Scopus, Science Direct and Springer Link to gather raw data from publications up to March 2021, using terms such as 'natural products', marine, micro-organism, and animal, COVID-19. We extracted a number of documented clinical trials of products that were tested in silico, in vitro, and in vivo which paid specific attention to chemical profiles and mechanisms of action.
Results: Various classes of flavonoids, 2 polyphenols, peptides and tannins were found, which exhibit inhibitory properties against viral and host proteins, including 3CLpro, PLpro, S, hACE2, and NF-κB, many of which are in different phases of clinical trials.
Discussion and conclusions: The synergistic effects of logical combinations with different mechanisms of action emphasizes their value in COVID19 management, such as iota carrageenan nasal spray, ermectin oral drops, omega-3 supplementation, and a quadruple treatment of zinc, quercetin, bromelain, and vitamin C. Though in vivo efficacy of these compounds has yet to be established, these bioproducts are potentially useful in counteracting the effects of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2coronavirus; combination treatment; microorganisms; pandemic; target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in the present article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New Hopes for Drugs against COVID-19 Come from the Sea.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 11;19(2):104. doi: 10.3390/md19020104. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33670191 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products with Tandem Anti-inflammatory, Immunomodulatory and Anti-SARS-CoV/2 Effects: A Drug Discovery Perspective against SARS-CoV-2.Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(14):2530-2564. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210726094955. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34313197
-
Current Landscape of Natural Products against Coronaviruses: Perspectives in COVID-19 Treatment and Anti-viral Mechanism.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(41):5241-5260. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201106093912. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 33155902 Review.
-
Development of Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents-Inspiration from Immunomodulatory Natural Products.Viruses. 2021 Jun 28;13(7):1257. doi: 10.3390/v13071257. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34203182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteamine with In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Immunomodulatory Effects Has the Potential to Be a Repurposing Drug Candidate for COVID-19 Therapy.Cells. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):52. doi: 10.3390/cells11010052. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011614 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bioactive natural products in COVID-19 therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 19;13:926507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.926507. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36059994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the Power of Venomous Animal-Derived Toxins against COVID-19.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;15(2):159. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020159. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing Applied to the Study of Natural Products and Extracts That Modulate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/ACE2 Interaction.Molecules. 2023 Dec 13;28(24):8072. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248072. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdo N, Moheyeldin O, Shehata MG, El Sohaimy S.. 2021. Inhibition of COVID-19 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by natural bioactive compounds: molecular docking analysis. Egypt J Chem. 64:1989–2001.
-
- Agrawal PK, Agrawal C, Blunden G.. 2020. Quercetin: antiviral significance and possible COVID-19 integrative considerations. Nat Prod Commun. 15(12):1934578X2097629–1934578X20976293.
-
- Agrawal PK, Agrawal C, Blunden G.. 2021. Rutin: a potential antiviral for repurposing as a SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitor. Nat Prod Commun. 16(4):19.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous