Annexin A1 Is a Potential Prognostic Marker for, and Enhances the Metastasis of, Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 35225485
- PMCID: PMC9272612
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.2.715
Annexin A1 Is a Potential Prognostic Marker for, and Enhances the Metastasis of, Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Annexin A1 (ANXA1) is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein which contributes to proliferation, cancer progression and metastasis. Overexpression of ANXA1 is closely associated with metastasis in numerous types of cancer. Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a bile-duct cancer which has high rates of metastasis. Previously, we demonstrated up-regulation of ANXA1 in a highly metastatic CCA cell line (KKU-213AL5). Here, we investigated the functions of ANXA1 in the progression of CCA cell lines and evaluated its clinical impacts in human CCA tissues. Methods: Effects of ANXA1 on metastatic potential of CCA cell lines were evaluated using cell-proliferation, clonogenic, migration and invasion assays. The expression of ANXA1 in 44 intrahepatic human CCA tissues was investigated using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The association of ANXA1 with clinicopathological features of CCA patients was analyzed.
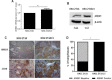
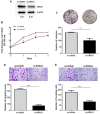
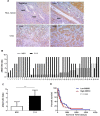
Results: Silencing of ANXA1 expression using siRNA significantly decreased cell proliferation, colony formation, cell migration and invasion in the KKU-213AL5 cell line. IHC results showed low expression of ANXA1 in normal bile ducts in the non-tumor area. In contrast, high expression of ANXA1 in human CCA tissues was associated with advanced tumor stage, tumor size and presence of lymph-node metastasis.
Conclusion: These findings strongly imply that ANXA1 contributes to the progression of CCA. ANXA1 can serve as a potential prognostic marker for CCA. Ablation of ANXA1 action may be an alternative strategy to prevent metastasis of CCA.
Keywords: ANXA1; Annexin A1; Metastasis; cholangiocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Annexin A1: A new immunohistological marker of cholangiocarcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Apr 28;19(16):2456-65. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i16.2456. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23674846 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptor protein XB130 regulates the aggressiveness of cholangiocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 15;16(11):e0259075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259075. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34780466 Free PMC article.
-
miR-378 serves as a prognostic biomarker in cholangiocarcinoma and promotes tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion.Cancer Biomark. 2019;24(2):173-181. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181980. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 30594918
-
The Role of microRNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 16;22(14):7627. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147627. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA in cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Sep;249:154755. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154755. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37651837 Review.
Cited by
-
Current State of Knowledge on Blood and Tissue-Based Biomarkers for Opisthorchis viverrini-induced Cholangiocarcinoma: A Review of Prognostic, Predictive, and Diagnostic Markers.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Jan 1;25(1):25-41. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.1.25. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38285765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Babbin BA, Lee WY, Parkos CA, et al. Annexin I regulates SKCO-15 cell invasion by signaling through formyl peptide receptors. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:19588–99. - PubMed
-
- Bist P, Leow SC, Phua QH, et al. Annexin-1 interacts with NEMO and RIP1 to constitutively activate IKK complex and NF-kappaB: implication in breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene. 2011;30:3174–85. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

