Global and context-specific transcriptional consequences of oncogenic Fbw7 mutations
- PMID: 35225231
- PMCID: PMC8926403
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.74338
Global and context-specific transcriptional consequences of oncogenic Fbw7 mutations
Abstract
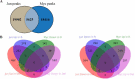
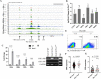
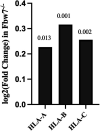
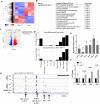
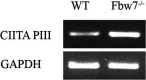
The Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase targets many proteins for proteasomal degradation, which include oncogenic transcription factors (TFs) (e.g., c-Myc, c-Jun, and Notch). Fbw7 is a tumor suppressor and tumors often contain mutations in FBXW7, the gene that encodes Fbw7. The complexity of its substrate network has obscured the mechanisms of Fbw7-associated tumorigenesis, yet this understanding is needed for developing therapies. We used an integrated approach employing RNA-Seq and high-resolution mapping (cleavage under target and release using nuclease) of histone modifications and TF occupancy (c-Jun and c-Myc) to examine the combinatorial effects of misregulated Fbw7 substrates in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells with engineered tumor-associated FBXW7 null or missense mutations. Both Fbw7 mutations caused widespread transcriptional changes associated with active chromatin and altered TF occupancy: some were common to both Fbw7 mutant cell lines, whereas others were mutation specific. We identified loci where both Jun and Myc were coregulated by Fbw7, suggesting that substrates may have synergistic effects. One coregulated gene was CIITA, the master regulator of MHC Class II gene expression. Fbw7 loss increased MHC Class II expression and Fbw7 mutations were correlated with increased CIITA expression in TCGA colorectal tumors and cell lines, which may have immunotherapeutic implications for Fbw7-associated cancers. Analogous studies in neural stem cells in which FBXW7 had been acutely deleted closely mirrored the results in CRC cells. Gene set enrichment analyses revealed Fbw7-associated pathways that were conserved across both cell types that may reflect fundamental Fbw7 functions. These analyses provide a framework for understanding normal and neoplastic context-specific Fbw7 functions.
Keywords: Fbw7; Jun; Myc; cancer biology; chromatin; chromosomes; gene expression; human; transcription factors; ubiquitin.
© 2022, Thirmanne et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HT, FW, DJ, JS, AD, HF, RA, RG, PP, SH, BC No competing interests declared
Figures


Similar articles
-
F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 regulates intestinal cell lineage commitment and is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor.Gastroenterology. 2010 Sep;139(3):929-41. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.05.078. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20638938
-
FBW7 mutations mediate resistance of colorectal cancer to targeted therapies by blocking Mcl-1 degradation.Oncogene. 2017 Feb 9;36(6):787-796. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.247. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27399335 Free PMC article.
-
The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):9085-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402770101. Epub 2004 May 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15150404 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant regulation of FBW7 in cancer.Oncotarget. 2014 Apr 30;5(8):2000-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1859. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24899581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: mechanisms and opportunities.Cancer Cell. 2014 Oct 13;26(4):455-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.013. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 25314076 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional analysis reveals driver cooperativity and novel mechanisms in endometrial carcinogenesis.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Oct 11;15(10):e17094. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202217094. Epub 2023 Aug 17. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37589076 Free PMC article.
-
A germline point mutation in the MYC-FBW7 phosphodegron initiates hematopoietic malignancies.Genes Dev. 2024 Apr 17;38(5-6):253-272. doi: 10.1101/gad.351292.123. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 38565249 Free PMC article.
-
A Virus-Packageable CRISPR System Identifies Host Dependency Factors Co-Opted by Multiple HIV-1 Strains.mBio. 2023 Feb 28;14(1):e0000923. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00009-23. Epub 2023 Feb 6. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36744886 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights and clinical implications for the tumor suppressor role of SCFFBXW7 E3 ubiquitin ligase.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Sep;1879(5):189140. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189140. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38909632 Review.
-
Erythropoietin regulates energy metabolism through EPO-EpoR-RUNX1 axis.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 16;15(1):8114. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52352-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39284834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N, Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ, Lehár J, Kryukov GV, Sonkin D, Reddy A, Liu M, Murray L, Berger MF, Monahan JE, Morais P, Meltzer J, Korejwa A, Jané-Valbuena J, Mapa FA, Thibault J, Bric-Furlong E, Raman P, Shipway A, Engels IH, Cheng J, Yu GK, Yu J, Aspesi P, Jr, de Silva M, Jagtap K, Jones MD, Wang L, Hatton C, Palescandolo E, Gupta S, Mahan S, Sougnez C, Onofrio RC, Liefeld T, MacConaill L, Winckler W, Reich M, Li N, Mesirov JP, Gabriel SB, Getz G, Ardlie K, Chan V, Myer VE, Weber BL, Porter J, Warmuth M, Finan P, Harris JL, Meyerson M, Golub TR, Morrissey MP, Sellers WR, Schlegel R, Garraway LA. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature. 2012;483:603–607. doi: 10.1038/nature11003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bressan RB, Dewari PS, Kalantzaki M, Gangoso E, Matjusaitis M, Garcia-Diaz C, Blin C, Grant V, Bulstrode H, Gogolok S, Skarnes WC, Pollard SM. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-assisted gene targeting enables rapid and precise genetic manipulation of mammalian neural stem cells. Development (Cambridge, England) 2017;144:635–648. doi: 10.1242/dev.140855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

