Defective repair of topoisomerase I induced chromosomal damage in Huntington's disease
- PMID: 35224690
- PMCID: PMC8882575
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04204-6
Defective repair of topoisomerase I induced chromosomal damage in Huntington's disease
Abstract
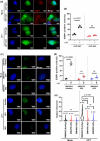
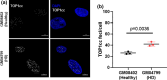
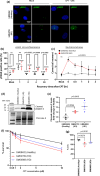
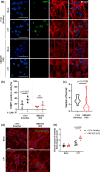
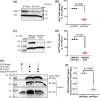
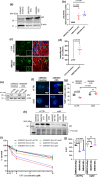
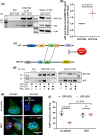
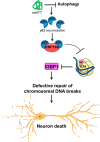
Topoisomerase1 (TOP1)-mediated chromosomal breaks are endogenous sources of DNA damage that affect neuronal genome stability. Whether TOP1 DNA breaks are sources of genomic instability in Huntington's disease (HD) is unknown. Here, we report defective 53BP1 recruitment in multiple HD cell models, including striatal neurons derived from HD patients. Defective 53BP1 recruitment is due to reduced H2A ubiquitination caused by the limited RNF168 activity. The reduced availability of RNF168 is caused by an increased interaction with p62, a protein involved in selective autophagy. Depletion of p62 or disruption of the interaction between RNAF168 and p62 was sufficient to restore 53BP1 enrichment and subsequent DNA repair in HD models, providing new opportunities for therapeutic interventions. These findings are reminiscent to what was described for p62 accumulation caused by C9orf72 expansion in ALS/FTD and suggest a common mechanism by which protein aggregation perturb DNA repair signaling.
Keywords: Chromatin ubiquitination; DNA repair; Huntington’s disease; RNF168; TOP1cc; p62/SQSTM1.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing/ conflicting interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
USP14 regulates DNA damage repair by targeting RNF168-dependent ubiquitination.Autophagy. 2018;14(11):1976-1990. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1496877. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29995557 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy Regulates Chromatin Ubiquitination in DNA Damage Response through Elimination of SQSTM1/p62.Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 7;63(1):34-48. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.027. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27345151
-
RNF126 Quenches RNF168 Function in the DNA Damage Response.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018 Dec;16(6):428-438. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30529286 Free PMC article.
-
New answers to the old RIDDLE: RNF168 and the DNA damage response pathway.FEBS J. 2022 May;289(9):2467-2480. doi: 10.1111/febs.15857. Epub 2021 Apr 16. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33797206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory ubiquitylation in response to DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Apr 5;8(4):436-43. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.01.013. Epub 2009 Feb 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 19230794 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and detection of DNA-protein crosslinks in mammalian cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 25;52(2):525-547. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1178. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38084926 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal protein post-translational modifications induces aggregation and abnormal deposition of protein, mediating neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Biosci. 2024 Feb 12;14(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01189-y. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38347638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly ADP-ribose signaling is dysregulated in Huntington disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct;121(40):e2318098121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2318098121. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39331414
-
High Glucose Increases DNA Damage and Elevates the Expression of Multiple DDR Genes.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;14(1):144. doi: 10.3390/genes14010144. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672885 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

