A high-efficiency and versatile CRISPR/Cas9-mediated HDR-based biallelic editing system
- PMID: 35187887
- PMCID: PMC8861562
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2100196
A high-efficiency and versatile CRISPR/Cas9-mediated HDR-based biallelic editing system
Abstract
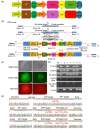
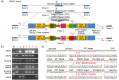
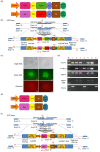
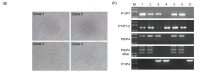
Clustered regulatory interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 nuclease (Cas9), the third-generation genome editing tool, has been favored because of its high efficiency and clear system composition. In this technology, the introduced double-strand breaks (DSBs) are mainly repaired by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR) pathways. The high-fidelity HDR pathway is used for genome modification, which can introduce artificially controllable insertions, deletions, or substitutions carried by the donor templates. Although high-level knock-out can be easily achieved by NHEJ, accurate HDR-mediated knock-in remains a technical challenge. In most circumstances, although both alleles are broken by endonucleases, only one can be repaired by HDR, and the other one is usually recombined by NHEJ. For gene function studies or disease model establishment, biallelic editing to generate homozygous cell lines and homozygotes is needed to ensure consistent phenotypes. Thus, there is an urgent need for an efficient biallelic editing system. Here, we developed three pairs of integrated selection systems, where each of the two selection cassettes contained one drug-screening gene and one fluorescent marker. Flanked by homologous arms containing the mutated sequences, the selection cassettes were integrated into the target site, mediated by CRISPR/Cas9-induced HDR. Positively targeted cell clones were massively enriched by fluorescent microscopy after screening for drug resistance. We tested this novel method on the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin 1 (PSEN1) loci and demonstrated up to 82.0% biallelic editing efficiency after optimization. Our results indicate that this strategy can provide a new efficient approach for biallelic editing and lay a foundation for establishment of an easier and more efficient disease model.
Keywords: Biallelic editing; CRISPR/Cas9; Homology-directed repair (HDR); Homozygote.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methods Favoring Homology-Directed Repair Choice in Response to CRISPR/Cas9 Induced-Double Strand Breaks.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6461. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186461. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9-based knock-in approaches in zebrafish.Methods. 2017 May 15;121-122:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28300641 Review.
-
Precision genome editing in the CRISPR era.Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;95(2):187-201. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0137. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28177771 Review.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 fusion to dominant-negative 53BP1 enhances HDR and inhibits NHEJ specifically at Cas9 target sites.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 28;10(1):2866. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10735-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31253785 Free PMC article.
-
Highly efficient CRISPR/HDR-mediated knock-in for mouse embryonic stem cells and zygotes.Biotechniques. 2015 Oct 1;59(4):201-2, 204, 206-8. doi: 10.2144/000114339. eCollection 2015 Oct. Biotechniques. 2015. PMID: 26458548
Cited by
-
Antiretrovirals to CCR5 CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing - A paradigm shift chasing an HIV cure.Clin Immunol. 2023 Oct;255:109741. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109741. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37611838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-locus, dual-HDR editing permits efficient generation of antigen-specific regulatory T cells with robust suppressive activity.Mol Ther. 2023 Oct 4;31(10):2872-2886. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.07.016. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37481700 Free PMC article.
-
A dominant dpy-10 co-transformation marker using CRISPR/Cas9 and a linear repair template in Caenorhabditis tropicalis.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Nov 3;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000900. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000900. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 38021174 Free PMC article.
-
RNA therapeutics to control fibrinolysis: review on applications in biology and medicine.J Thromb Haemost. 2024 Aug;22(8):2103-2114. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.04.006. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 38663489 Review.
-
Enrichment strategies to enhance genome editing.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Jul 1;30(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00943-1. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37393268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

