Immune and Metabolic Alterations in Liver Fibrosis: A Disruption of Oxygen Homeostasis?
- PMID: 35187072
- PMCID: PMC8850363
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.802251
Immune and Metabolic Alterations in Liver Fibrosis: A Disruption of Oxygen Homeostasis?
Abstract
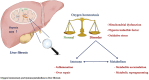
According to the WHO, "cirrhosis of the liver" was the 11th leading cause of death globally in 2019. Many kinds of liver diseases can develop into liver cirrhosis, and liver fibrosis is the main pathological presentation of different aetiologies, including toxic damage, viral infection, and metabolic and genetic diseases. It is characterized by excessive synthesis and decreased decomposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Hepatocyte cell death, hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, and inflammation are crucial incidences of liver fibrosis. The process of fibrosis is also closely related to metabolic and immune disorders, which are usually induced by the destruction of oxygen homeostasis, including mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and hypoxia pathway activation. Mitochondria are important organelles in energy generation and metabolism. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are key factors activated when hypoxia occurs. Both are considered essential factors of liver fibrosis. In this review, the authors highlight the impact of oxygen imbalance on metabolism and immunity in liver fibrosis as well as potential novel targets for antifibrotic therapies.
Keywords: hypoxia-inducible factor; immunometabolism; liver fibrosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Wang, Zhuang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Serine Protease HtrA2/Omi Deficiency Impairs Mitochondrial Homeostasis and Promotes Hepatic Fibrogenesis via Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells.Cells. 2019 Sep 20;8(10):1119. doi: 10.3390/cells8101119. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31547195 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies Targeting the Innate Immune Response for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Liver Fibrosis.Drugs. 2021 Mar;81(4):419-443. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01458-x. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33400242 Review.
-
Role of NADPH oxidases in the redox biology of liver fibrosis.Redox Biol. 2015 Dec;6:106-111. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26204504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver fibrosis: from the bench to clinical targets.Dig Liver Dis. 2004 Apr;36(4):231-42. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2004.01.003. Dig Liver Dis. 2004. PMID: 15115333 Review.
Cited by
-
Endpoints in NASH Clinical Trials: Are We Blind in One Eye?Metabolites. 2024 Jan 8;14(1):40. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010040. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38248843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Metabolic Dysfunction Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 15;24(24):17514. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417514. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SKIL/SnoN attenuates TGF-β1/SMAD signaling-dependent collagen synthesis in hepatic fibrosis.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Nov 3;23(6):1014-1025. doi: 10.17305/bb.2023.9000. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37389959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai W.-L., Dong L.-y., Wang J., Li Z.-w., Wang X., Gao J., et al. (2018). Deficiency in Augmenter of Liver Regeneration Accelerates Liver Fibrosis by Promoting Migration of Hepatic Stellate Cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Bba) - Mol. Basis Dis. 1864, 3780–3791. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.09.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

