The nonstructural protein NSs encoded by tomato zonate spot virus suppresses RNA silencing by interacting with NbSGS3
- PMID: 35184365
- PMCID: PMC8995058
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13192
The nonstructural protein NSs encoded by tomato zonate spot virus suppresses RNA silencing by interacting with NbSGS3
Abstract
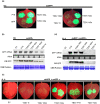
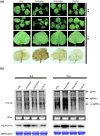
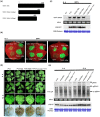
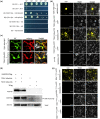
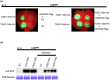
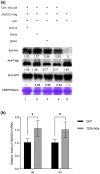
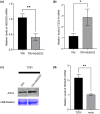
Viral suppressors of RNA silencing (VSRs) are encoded by diverse viruses to counteract the RNA silencing-mediated defence mounted by the virus-infected host cells. In this study, we identified the NSs protein encoded by tomato zonate spot virus (TZSV) as a potent VSR, and used a potato virus X (PVX)-based heterologous expression system to demonstrate TZSV NSs as a viral pathogenicity factor that intensified PVX symptoms in Nicotiana benthamiana. We then used a yeast two-hybrid screen to identify the suppressor of gene silencing 3 protein of N. benthamiana (NbSGS3), a known component of the plant RNA silencing pathway, as an interaction partner of TZSV NSs. We verified this interaction in plant cells with bimolecular fluorescence complementation, subcellular colocalization, and co-immunoprecipitation. We further revealed that the NSs-NbSGS3 interaction correlated with the VSR activity of TZSV NSs. TZSV NSs reduced the concentration of NbSGS3 protein in plant cells, probably through the ubiquitination and autophagy pathways. Interestingly, TZSV infection, but not NSs overexpression, significantly up-regulated the NbSGS3 transcript levels. Our data indicate that TZSV NSs suppresses RNA silencing of the host plant and enhances TZSV pathogenicity through its interaction with NbSGS3. This study reveals a novel molecular mechanism of NSs-mediated suppression of plant host antiviral defence.
Keywords: Suppressor of gene silencing 3; RNA silencing; VSRs; nonstructural protein NSs; tomato zonate spot virus (TZSV).
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of the nonstructural protein NSs of tomato zonate spot virus.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 24;17(1):e0262194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262194. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35073345 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Stripe Mosaic Virus-Encoded P4 Is a Weak Suppressor of Viral RNA Silencing and Is Required for Disease Symptom Development.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2020 Mar;33(3):412-422. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-08-19-0239-IA. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2020. PMID: 31841359
-
RNA silencing-related genes contribute to tolerance of infection with potato virus X and Y in a susceptible tomato plant.Virol J. 2020 Oct 8;17(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01414-x. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 33032637 Free PMC article.
-
The Heterologous Expression of the p22 RNA Silencing Suppressor of the Crinivirus Tomato Chlorosis Virus from Tobacco Rattle Virus and Potato Virus X Enhances Disease Severity but Does Not Complement Suppressor-Defective Mutant Viruses.Viruses. 2017 Nov 24;9(12):358. doi: 10.3390/v9120358. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29186781 Free PMC article.
-
A calmodulin-like protein suppresses RNA silencing and promotes geminivirus infection by degrading SGS3 via the autophagy pathway in Nicotiana benthamiana.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Feb 17;13(2):e1006213. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006213. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28212430 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Turnip crinkle virus-encoded suppressor of RNA silencing interacts with Arabidopsis SGS3 to enhance virus infection.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Feb;24(2):154-166. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13282. Epub 2022 Nov 26. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36433724 Free PMC article.
-
P3/P3N-PIPO of PVY interacting with BI-1 inhibits the degradation of NIb by ATG6 to facilitate virus replication in N. benthamiana.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Apr 17;14:1183144. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1183144. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37139112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Csorba, T. , Kontra, L. & Burgyan, J. (2015) viral silencing suppressors: tools forged to fine‐tune host–pathogen coexistence. Virology, 479–480, 85–103. - PubMed
-
- Dalmay, T. , Hamilton, A. , Rudd, S. , Angell, S. & Baulcombe, D.C. (2000) An RNA‐dependent RNA polymerase gene in Arabidopsis is required for posttranscriptional gene silencing mediated by a transgene but not by a virus. Cell, 101, 543–553. - PubMed
-
- Ding, S.W. (2010) RNA‐based antiviral immunity. Nature Reviews Immunology, 10, 632–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

