Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 impairs sumoylation
- PMID: 35181598
- PMCID: PMC8860096
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202101103
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 impairs sumoylation
Abstract
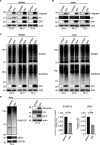
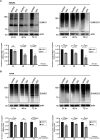
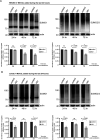
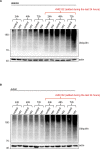
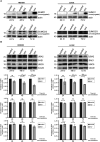
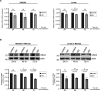
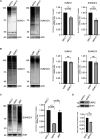
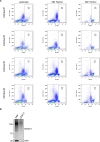
During infection, the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) manipulates host cell mechanisms to its advantage, thereby controlling its replication or latency, and evading immune responses. Sumoylation is an essential post-translational modification that controls vital cellular activities including proliferation, stemness, or anti-viral immunity. SUMO peptides oppose pathogen replication and mediate interferon-dependent anti-viral activities. In turn, several viruses and bacteria attack sumoylation to disarm host immune responses. Here, we show that HIV-1 impairs cellular sumoylation and targets the host SUMO E1-activating enzyme. HIV-1 expression in cultured HEK293 cells or in CD4+ Jurkat T lymphocytes diminishes sumoylation by both SUMO paralogs, SUMO1 and SUMO2/3. HIV-1 causes a sharp and specific decline in UBA2 protein levels, a subunit of the heterodimeric SUMO E1 enzyme, which likely serves to reduce the efficiency of global protein sumoylation. Furthermore, HIV-1-infected individuals display a significant reduction in total leukocyte sumoylation that is uncoupled from HIV-induced cytopenia. Because sumoylation is vital for immune function, T-cell expansion and activity, loss of sumoylation during HIV disease may contribute to immune system deterioration in patients.
© 2022 Mete et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Viruses, SUMO, and immunity: the interplay between viruses and the host SUMOylation system.J Neurovirol. 2021 Aug;27(4):531-541. doi: 10.1007/s13365-021-00995-9. Epub 2021 Aug 3. J Neurovirol. 2021. PMID: 34342851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncovalent SUMO-interaction motifs in HIV integrase play important roles in SUMOylation, cofactor binding, and virus replication.Virol J. 2019 Apr 2;16(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1134-8. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 30940169 Free PMC article.
-
Ang II Promotes SUMO2/3 Modification of RhoGDI1 Through Aos1 and Uba2 Subunits, and then Regulates RhoGDI1 Stability and Cell Proliferation.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021 Aug;35(4):769-773. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07173-3. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021. PMID: 33891248
-
Evaluation of the interactions of HIV-1 integrase with small ubiquitin-like modifiers and their conjugation enzyme Ubc9.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Nov;30(5):1053-60. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1088. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22895527
-
The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2018 Apr;52(4):1081-1094. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4280. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complex Relationships between HIV-1 Integrase and Its Cellular Partners.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 15;23(20):12341. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012341. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
