Chromosome-scale assembly and population diversity analyses provide insights into the evolution of Sapindus mukorossi
- PMID: 35178562
- PMCID: PMC8854635
- DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhac012
Chromosome-scale assembly and population diversity analyses provide insights into the evolution of Sapindus mukorossi
Abstract
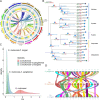
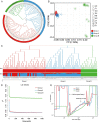
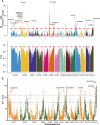
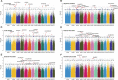
Sapindus mukorossi is an environmentally friendly plant and renewable energy source whose fruit has been widely used for biomedicine, biodiesel, and biological chemicals due to its richness in saponin and oil contents. Here, we report the first chromosome-scale genome assembly of S. mukorossi (covering ~391 Mb with a scaffold N50 of 24.66 Mb) and characterize its genetic architecture and evolution by resequencing 104 S. mukorossi accessions. Population genetic analyses showed that genetic diversity in the southwestern distribution area was relatively higher than that in the northeastern distribution area. Gene flow events indicated that southwest species may be the donor population for the distribution areas in China. Genome-wide selective sweep analysis showed that a large number of genes are involved in defense responses, growth and development, including SmRPS2, SmRPS4, SmRPS7, SmNAC2, SmNAC23, SmNAC102, SmWRKY6, SmWRKY26, and SmWRKY33. We also identified several candidate genes controlling six agronomic traits by genome-wide association studies, including SmPCBP2, SmbHLH1, SmCSLD1, SmPP2C, SmLRR-RKs, and SmAHP. Our study not only provides a rich genomic resource for further basic research on Sapindaceae woody trees but also identifies several economically significant genes for genomics-enabled improvements in molecular breeding.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nanjing Agricultural University.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic Diversity Analysis of Sapindus in China and Extraction of a Core Germplasm Collection Using EST-SSR Markers.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 24;13:857993. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.857993. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35685004 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the potential global distribution of Sapindus mukorossi under climate change based on MaxEnt modelling.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Mar;29(15):21751-21768. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17294-9. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34773237
-
Saponin fraction from Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn as a novel cosmetic additive: Extraction, biological evaluation, analysis of anti-acne mechanism and toxicity prediction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113552. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113552. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33152431
-
Effects of Sapindus mukorossi Seed Oil on Skin Wound Healing: In Vivo and in Vitro Testing.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 26;20(10):2579. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102579. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31130677 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological effects of Sapindus mukorossi.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2012 Sep-Oct;54(5):273-80. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46652012000500007. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2012. PMID: 22983291 Review.
Cited by
-
The Chromosome-level genome of Aesculus wilsonii provides new insights into terpenoid biosynthesis and Aesculus evolution.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 18;13:1022169. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1022169. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388583 Free PMC article.
-
The Biosynthesis Pattern and Transcriptome Analysis of Sapindus saponaria Oil.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;13(13):1781. doi: 10.3390/plants13131781. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999621 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the fermentation filtrate from soapberry (Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn.) pericarp on improving the microbial diversity and composition of the human scalp.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1443767. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1443767. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39450286 Free PMC article.
-
Diversification of FT-like genes in the PEBP family contributes to the variation of flowering traits in Sapindaceae species.Mol Hortic. 2024 Jul 16;4(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s43897-024-00104-4. Mol Hortic. 2024. PMID: 39010247 Free PMC article.
-
Application of High-Throughput Sequencing on the Chinese Herbal Medicine for the Data-Mining of the Bioactive Compounds.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 14;13:900035. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.900035. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35909744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goyal S, Kumar D, Menaria Get al. . Medicinal plants of the genus Sapindus (Sapindaceae) – a review of their botany, phytochemistry, biological activity and traditional uses. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2014;4:7–20.
-
- Li SZ. The Compendium of Materia Medica. People’s Medical Publishing House; 1982.
-
- Zhu S, Fang PJ. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 1959.
-
- Shao WH. Geographic variation of saponins contents in Sapindus mukorossi peels from different habitats. Bull Bot Res. 2012;32:627–31.
-
- Rupeshkumar G, Surekha SK, Balu CAet al. . Study of functional properties of Sapindus mukorossi as a potential bio-surfactant. Indian J Sci Technol. 2011;4:530–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

