Estrogen-mediated downregulation of HIF-1α signaling in B lymphocytes influences postmenopausal bone loss
- PMID: 35177582
- PMCID: PMC8854586
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-022-00189-x
Estrogen-mediated downregulation of HIF-1α signaling in B lymphocytes influences postmenopausal bone loss
Abstract
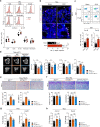
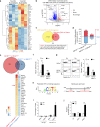
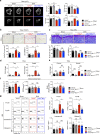
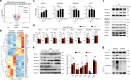
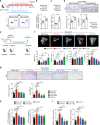
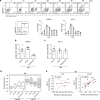
In the bone marrow, B cells and bone-resorbing osteoclasts colocalize and form a specific microenvironment. How B cells functionally influence osteoclasts and bone architecture is poorly understood. Using genetically modified mice and high-throughput analyses, we demonstrate that prolonged HIF-1α signaling in B cells leads to enhanced RANKL production and osteoclast formation. In addition, deletion of HIF-1α in B cells prevents estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss in mice. Mechanistically, estrogen controls HIF-1α protein stabilization through HSP70-mediated degradation in bone marrow B cells. The stabilization of HIF-1α protein in HSP70-deficient bone marrow B cells promotes RANKL production and osteoclastogenesis. Induction of HSP70 expression by geranylgeranylacetone (GGA) administration alleviates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Moreover, RANKL gene expression has a positive correlation with HIF1A expression in human B cells. In conclusion, HIF-1α signaling in B cells is crucial for the control of osteoclastogenesis, and the HSP70/HIF-1α axis may serve as a new therapeutic target for osteoporosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.Bone. 2015 Jun;75:128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25708053
-
Dimethyloxalylglycine prevents bone loss in ovariectomized C57BL/6J mice through enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e112744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112744. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25394221 Free PMC article.
-
Alisol-B, a novel phyto-steroid, suppresses the RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and prevents bone loss in mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Aug 1;80(3):352-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.04.014. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20412788
-
[Research on Relationship of HIF-1 Signaling Pathway and Postmenstrual Osteoporosis].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Nov;48(6):862-868. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 29260521 Chinese.
-
Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar;123:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.05.014. Epub 2021 May 20. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34024716 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of IRF9 Promotes Osteoclast Differentiation by Decreased Ferroptosis via STAT3 Activation.Inflammation. 2024 Feb;47(1):99-113. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01896-1. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 37804406
-
Cannabidiol Decreases Intestinal Inflammation in the Ovariectomized Murine Model of Postmenopause.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 28;11(1):74. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010074. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672582 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Feedback Regulation of Circular RNA Hsa_circ_0000566 and HIF-1α promotes Osteosarcoma Progression and Glycolysis Metabolism.Aging Dis. 2023 Apr 1;14(2):529-547. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0826. eCollection 2023 Apr 1. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37008055 Free PMC article.
-
A causal relationship between bone mineral density and breast cancer risk: a mendelian randomization study based on east Asian population.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 14;24(1):1148. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12908-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39277718 Free PMC article.
-
The Bioactive Compounds of Epimedium and Their Potential Mechanism of Action in Treating Osteoporosis: A Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 29;17(6):706. doi: 10.3390/ph17060706. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931373 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

