Celecoxib Synergistically Enhances MLN4924-Induced Cytotoxicity and EMT Inhibition Via AKT and ERK Pathways in Human Urothelial Carcinoma
- PMID: 35176901
- PMCID: PMC8859662
- DOI: 10.1177/09636897221077921
Celecoxib Synergistically Enhances MLN4924-Induced Cytotoxicity and EMT Inhibition Via AKT and ERK Pathways in Human Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
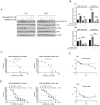
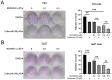
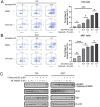
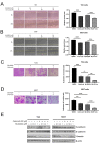
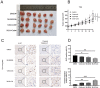
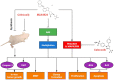
MLN4924 is a specific small-molecule inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) that blocks the neddylation modification cascade. Several I/II/III clinical trials suggested that MLN4924 exerts an antitumor effect against various malignancies. However, recent studies have also found that MLN4924 activates the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signal pathways, important regulators of tumorigenesis, and drug resistance in human urothelial carcinoma (UC). This study examined the synergistic effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) selective inhibitor, on MLN4924-induced cytotoxicity and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) inhibition via AKT and ERK pathways in human UC. We performed both in vitro and in vivo experiments. Briefly, a combination of MLN4924 and celecoxib reduced the protein expression of p-AKT(S473) and p-ERK in UC cell lines. Moreover, celecoxib shifted the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) curve of MLN4924 to the left, and the combinational effect of MLN4924 and celecoxib showed significant synergism in T24 and 5637 cells. Also, celecoxib enhanced the MLN4924 antitumor effects of inhibiting UC cell growth, colony formation, migration, invasion, and inducing apoptosis. In addition, celecoxib potentiated the MLN4924-induced EMT, decreased the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin, and activated the expression of E-cadherin. Celecoxib also increased the expression of pro-apoptosis proteins PARP and BAX and reduced the expression of antiapoptosis protein Bcl2. In vivo study indicated that the combination of MLN4924 and celecoxib synergistically suppressed the tumor growth in a UC xenograft nude-mice model, which was further supported by immunohistochemistry of tumor tissues. To sum up, our study revealed that celecoxib synergistically enhanced MLN4924-induced cytotoxicity and EMT inhibition in UC. It also inhibited the activation of AKT and ERK pathways, which were activated by MLN4924. These discoveries provide a new drug combination strategy for UC treatment.
Keywords: EMT; MLN4924; celecoxib; neddylation; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MLN4924 Synergistically Enhances Cisplatin-induced Cytotoxicity via JNK and Bcl-xL Pathways in Human Urothelial Carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 23;5:16948. doi: 10.1038/srep16948. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26592553 Free PMC article.
-
MLN4924, a novel protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human urothelial carcinoma: In vitro and in vivo studies.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jul 28;363(2):127-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25615422
-
AKT inhibitor MK-2206 sensitizes breast cancer cells to MLN4924, a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(16):2069-2079. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1515550. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 30198810 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation-Independent Activities of MLN4924.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:363-372. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_21. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898238 Review.
-
Natural products and derivatives in renal, urothelial and testicular cancers: Targeting signaling pathways and therapeutic potential.Phytomedicine. 2024 May;127:155503. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155503. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38490077 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the role of neddylation in tumor microenvironment modulation: common outcome of multiple signaling pathways.Biomark Res. 2024 Jan 8;12(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00545-x. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 38191508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of NEDD8 NEDDylation induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via p53 signaling pathway.Biosci Rep. 2022 Aug 31;42(8):BSR20220994. doi: 10.1042/BSR20220994. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35880551 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in COPD induced by cigarette smoke: an update.Respir Res. 2022 Aug 31;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02153-z. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 36045410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational modifications: The potential ways for killing cancer stem cells.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 4;10(14):e34015. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34015. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39092260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting NEDD8-activating enzyme for cancer therapy: developments, clinical trials, challenges and future research directions.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jul 31;16(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01485-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37525282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Tan WS, Rodney S, Lamb B, Feneley M, Kelly J. Management of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a comprehensive analysis of guidelines from the United States, Europe and Asia. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;47:22–31. - PubMed
-
- Rajalingam K, Dikic I. SnapShot: expanding the ubiquitin code. Cell. 2016;164(5):1074.e1071. - PubMed
-
- Mansour MA. Ubiquitination: friend and foe in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;101:80–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

