Modeling the Structure and Interactions of Intrinsically Disordered Peptides with Multiple Replica, Metadynamics-Based Sampling Methods and Force-Field Combinations
- PMID: 35174713
- PMCID: PMC9097291
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.1c00889
Modeling the Structure and Interactions of Intrinsically Disordered Peptides with Multiple Replica, Metadynamics-Based Sampling Methods and Force-Field Combinations
Abstract
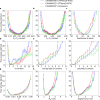
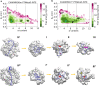
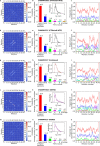
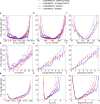
Intrinsically disordered proteins play a key role in many biological processes, including the formation of biomolecular condensates within cells. A detailed characterization of their configurational ensemble and structure-function paradigm is crucial for understanding their biological activity and for exploiting them as building blocks in material sciences. In this work, we incorporate bias-exchange metadynamics and parallel-tempering well-tempered metadynamics with CHARMM36m and CHARMM22* to explore the structural and thermodynamic characteristics of a short archetypal disordered sequence derived from a DEAD-box protein. The conformational landscapes emerging from our simulations are largely congruent across methods and force fields. Nevertheless, differences in fine details emerge from varying combinations of force-fields and sampling methods. For this protein, our analysis identifies features that help to explain the low propensity of this sequence to undergo self-association in vitro, which are common to all force-field/sampling method combinations. Overall, our work demonstrates the importance of using multiple force-field and sampling method combinations for accurate structural and thermodynamic information in the study of disordered proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2141:391-411. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0524-0_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32696368
-
Metadynamics Simulations to Study the Structural Ensembles and Binding Processes of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2405:169-178. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1855-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35298814
-
Sampling conformational space of intrinsically disordered proteins in explicit solvent: Comparison between well-tempered ensemble approach and solute tempering method.J Mol Graph Model. 2017 Mar;72:136-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2016.12.014. Epub 2016 Dec 28. J Mol Graph Model. 2017. PMID: 28092832
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Combined with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and/or Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Data for Characterizing Intrinsically Disordered Protein Conformational Ensembles.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 May 28;59(5):1743-1758. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00928. Epub 2019 Mar 18. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30840442 Review.
-
Computer Simulations of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2017 May 5;68:117-134. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-052516-050843. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2017. PMID: 28226222 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein compactness and interaction valency define the architecture of a biomolecular condensate across scales.Elife. 2023 Jul 20;12:e80038. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80038. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37470705 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerating Solvent Dynamics with Replica Exchange for Improved Free Energy Sampling.J Chem Theory Comput. 2023 Nov 14;19(21):7527-7532. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.3c00786. Epub 2023 Oct 21. J Chem Theory Comput. 2023. PMID: 37864561 Free PMC article.
-
Myofilament-associated proteins with intrinsic disorder (MAPIDs) and their resolution by computational modeling.Q Rev Biophys. 2023 Jan 11;56:e2. doi: 10.1017/S003358352300001X. Q Rev Biophys. 2023. PMID: 36628457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
