ASF1B: A Possible Prognostic Marker, Therapeutic Target, and Predictor of Immunotherapy in Male Thyroid Carcinoma
- PMID: 35174076
- PMCID: PMC8841667
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.678025
ASF1B: A Possible Prognostic Marker, Therapeutic Target, and Predictor of Immunotherapy in Male Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Thyroid carcinoma (TC) is the most common malignant endocrine tumor worldwide. Several studies have documented that male patients with TC have a higher rate of metastasis and disease recurrence than female patients. However, the mechanism underlying this observation is not completely clear. The goal of our research was to investigate the potential key candidate genes and pathways related to TC progression in male patients at the molecular level.
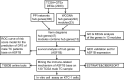
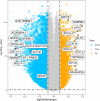
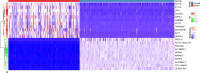
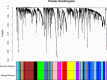
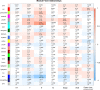
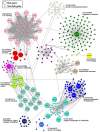
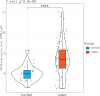
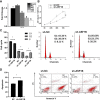
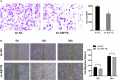
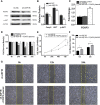
Methods: A total of 320 samples were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) databases. Hub genes were screened out using weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis. Survival analysis was used to identify hub genes associated with disease-free survival (DFS) rates. Estimation of STromal and Immune cells in MAlignant Tumor tissues using Expression (ESTIMATE) data were used to assess the relationship between hub genes and immune cell infiltration. The molecular mechanism and biological functions of hub genes were explored using RT-qPCR, Western blot, Cell Counting Kit-8 Assay, flow cytometry, Transwell assays, and scratch assays.
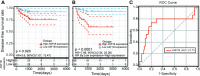
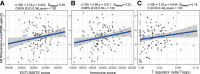
Results: Forty-seven hub genes were identified, and the survival analysis demonstrated that anti-silencing function 1B (ASF1B) was the sole independent risk factor for poor DFS in male TC patients. Possible associations between the results from the ESTIMATE analysis showed that the ASF1B expression level was related to the ESTIMATE score, immune score, and T-cell regulatory (Treg) infiltration level. Through in vitro cell function experiments, we verified that knockdown of ASF1B inhibited KTC-1 cell proliferation, promoted cell apoptosis, and blocked cell cycle. The silencing of ASF1B reduced protein kinase B (AKT), phospho-AKT (p-AKT), and forkhead box p3 (FOXP3) in KTC-1 cells. Moreover, FOXP3 overexpression markedly restored the cell migration, invasion, and proliferation abilities repressed by ASF1B knockdown.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that ASF1B can be considered a prognostic marker, therapeutic target, and predictor of immunotherapy response in male thyroid cancer patients. However, further in-depth studies are required to validate this finding.
Keywords: ASF1B; FOXP3; Treg; hub genes; male thyroid cancer; tumor immunity.
Copyright © 2022 Qiu, Wu, Shi, Liu, Li, Wu and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction of Novel lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Associated With Recurrence and Identification of Immune-Related Potential Regulatory Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 15;11:626663. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626663. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34336642 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis and the Regulatory Mechanism of ASF1B, a Gene Associated With Thyroid Cancer Prognosis in the Tumor Micro-Environment.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 20;11:711756. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.711756. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34490109 Free PMC article.
-
ASF1B is a Promising Prognostic Biomarker and Correlates With Immunotherapy Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 10;13:842351. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.842351. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35360875 Free PMC article.
-
ASF1B Serves as a Potential Therapeutic Target by Influencing Cell Cycle and Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 11;11:801506. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.801506. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35087760 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ASF1B as a prognostic marker for liver cancer by meta-analysis and its immune value revealed by a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of 33 human cancers.Prz Gastroenterol. 2023;18(3):249-265. doi: 10.5114/pg.2023.124423. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Prz Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37937108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum sex hormones correlate with pathological features of papillary thyroid cancer.Endocrine. 2024 Apr;84(1):148-154. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03554-w. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 37815746 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge mapping of immunotherapy for thyroid cancer from 1980 to 2022: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 29;102(39):e35506. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035506. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37773801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-24-3p Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and the Malignant Phenotype of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma by Regulating ASF1B Expression.Biochem Genet. 2023 Apr;61(2):742-761. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10278-5. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 36114946 Free PMC article.
-
Increased ASF1B Expression Correlates With Poor Prognosis in Patients With Gliomas.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 6;12:912101. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.912101. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875094 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroidectomy Using the Lateral Cervical Small Incision Approach for Early Thyroid Cancer.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022 Apr 20;15:713-720. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S358959. eCollection 2022. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35478775 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

