Stapled peptides as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the hACE2 receptor
- PMID: 35165970
- PMCID: PMC9111031
- DOI: 10.1002/psc.3409
Stapled peptides as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the hACE2 receptor
Abstract
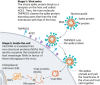
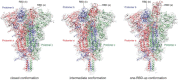
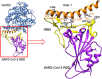
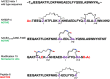
Stapled peptides are synthetic peptidomimetics of bioactive sites in folded proteins which carry chemical links, introduced during peptide synthesis, designed to retain the secondary structure in the native protein molecule. Stapled peptides have been investigated as potential modulators of protein-protein interactions for over two decades. The potential use of stapled peptides as inhibitors of viral entry, and therefore as antiviral therapeutics, has been established for several important viruses causing disease in humans, such as the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus. Several independent research initiatives have investigated the inhibitory effect of stapled peptides on binding of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19, to its receptor, angiotensin-converting-enzyme 2 (ACE2). These stapled peptides, which mimic Helix 1 of the human ACE2 receptor, have demonstrated mixed ability to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2 in cell-based studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; hACE2; inhibitor; peptide; stapling; therapeutic.
© 2022 European Peptide Society and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stapled Peptides Based on Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Potently Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro.mBio. 2020 Dec 11;11(6):e02451-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02451-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33310780 Free PMC article.
-
The TMPRSS2 Inhibitor Nafamostat Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Pulmonary Infection in Mouse Models of COVID-19.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0097021. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00970-21. Epub 2021 Aug 3. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34340553 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain with Stapled Peptides: An In Silico Study.J Phys Chem B. 2021 Jun 24;125(24):6572-6586. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c02398. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Phys Chem B. 2021. PMID: 34114829
-
Inhibition of S-protein RBD and hACE2 Interaction for Control of SARSCoV- 2 Infection (COVID-19).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):689-703. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201117111259. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208074 Review.
-
The expression of hACE2 receptor protein and its involvement in SARS-CoV-2 entry, pathogenesis, and its application as potential therapeutic target.Tumour Biol. 2021;43(1):177-196. doi: 10.3233/TUB-200084. Tumour Biol. 2021. PMID: 34420993 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of protein-binding peptides with controlled binding affinity: the case of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 derived peptides.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 5;10:1332359. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1332359. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38250735 Free PMC article.
-
Potential use of the S-protein-Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 binding pathway in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 28;10:1050034. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1050034. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36518573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schafmeister CE PJ, Verdine GL. An all‐hydrocarbon cross‐linking system for enhancing the helicity and metabolic stability of peptides. J am Chem Soc. 2000;122(24):5891‐5892. doi:10.1021/ja000563a - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
