A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice
- PMID: 35165440
- PMCID: PMC9170029
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04396-8
A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice
Abstract
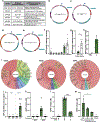
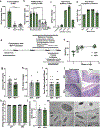
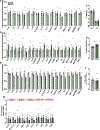
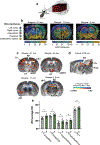
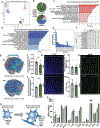
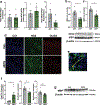
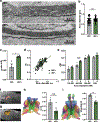
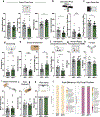
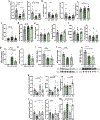
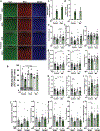
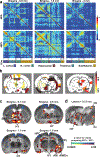
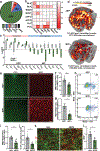
Integration of sensory and molecular inputs from the environment shapes animal behaviour. A major site of exposure to environmental molecules is the gastrointestinal tract, in which dietary components are chemically transformed by the microbiota1 and gut-derived metabolites are disseminated to all organs, including the brain2. In mice, the gut microbiota impacts behaviour3, modulates neurotransmitter production in the gut and brain4,5, and influences brain development and myelination patterns6,7. The mechanisms that mediate the gut-brain interactions remain poorly defined, although they broadly involve humoral or neuronal connections. We previously reported that the levels of the microbial metabolite 4-ethylphenyl sulfate (4EPS) were increased in a mouse model of atypical neurodevelopment8. Here we identified biosynthetic genes from the gut microbiome that mediate the conversion of dietary tyrosine to 4-ethylphenol (4EP), and bioengineered gut bacteria to selectively produce 4EPS in mice. 4EPS entered the brain and was associated with changes in region-specific activity and functional connectivity. Gene expression signatures revealed altered oligodendrocyte function in the brain, and 4EPS impaired oligodendrocyte maturation in mice and decreased oligodendrocyte-neuron interactions in ex vivo brain cultures. Mice colonized with 4EP-producing bacteria exhibited reduced myelination of neuronal axons. Altered myelination dynamics in the brain have been associated with behavioural outcomes7,9-14. Accordingly, we observed that mice exposed to 4EPS displayed anxiety-like behaviours, and pharmacological treatments that promote oligodendrocyte differentiation prevented the behavioural effects of 4EPS. These findings reveal that a gut-derived molecule influences complex behaviours in mice through effects on oligodendrocyte function and myelin patterning in the brain.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Targeting microbial metabolites to treat autism.Nat Med. 2022 Mar;28(3):448-450. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01711-8. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35165452 No abstract available.
-
Trust your gut, lest thou be anxious.Cell. 2022 Apr 14;185(8):1294-1296. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.035. Cell. 2022. PMID: 35427498
Similar articles
-
4-Ethylphenol-fluxes, metabolism and excretion of a gut microbiome derived neuromodulator implicated in autism.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Oct 12;10:1267754. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1267754. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37900921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mind-body connection: metabolite 4-ethylphenyl linked to anxiety behavior and oligodendrocyte modification in autism spectrum disorder.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Jun 1;324(6):G422-G425. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00221.2022. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36976795
-
Altered Schaedler flora mice: A defined microbiota animal model to study the microbiota-gut-brain axis.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 1;356:221-226. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.022. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30153465
-
Myelin as a regulator of development of the microbiota-gut-brain axis.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Jan;91:437-450. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33157256 Free PMC article.
-
The gut microbiota-oligodendrocyte axis: A promising pathway for modulating oligodendrocyte homeostasis and demyelination-associated disorders.Life Sci. 2024 Oct 1;354:122952. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122952. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39127317 Review.
Cited by
-
The gut microbiome in patients with Cushing's disease affects depression- and anxiety-like behavior in mice.Microbiome. 2024 Nov 1;12(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01939-1. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39482760
-
α-synuclein overexpression and the microbiome shape the gut and brain metabolome in mice.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Oct 30;10(1):208. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00816-w. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39477976 Free PMC article.
-
Limosilactobacillus-related 3-OMDP as a potential therapeutic target for depression.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2417179. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2417179. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39421970 Free PMC article.
-
Jiannao pills mitigate chronic restraint stress-induced anxiety in mice through the regulation of intestinal microflora.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4549-4563. doi: 10.62347/GEEW4432. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398613 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Lactobacillus murinus-derived small RNAs target porcine polyamine metabolism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 8;121(41):e2413241121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413241121. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39361652
References
-
- Swann JR et al. Application of 1H NMR spectroscopy to the metabolic phenotyping of rodent brain extracts: A metabonomic study of gut microbial influence on host brain metabolism. J Pharm Biomed Anal 143, 141–146 (2017). - PubMed
Method References:
-
- Holdeman Lillian V. & Moore WEC Anaerobe laboratory manual (4th ed). (Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 1977).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

