LncCDH5-3:3 Regulates Apoptosis, Proliferation, and Aggressiveness in Human Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35159188
- PMCID: PMC8834634
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11030378
LncCDH5-3:3 Regulates Apoptosis, Proliferation, and Aggressiveness in Human Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
(1) Lung cancer (both small cell and non-small cell) is the leading cause of new deaths associated with cancers globally in men and women. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are associated with tumorigenesis in different types of tumors, including lung cancer. Herein, we discuss: (1) An examination of the expression profile of lncCDH5-3:3 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and an evaluation of its functional role in lung cancer development and progression using in vitro models; (2) A quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay that confirms lncCDH5-3:3 expression in tumor samples resected from 20 NSCLC patients, and that shows its statistically higher expression levels at stage III NSCLC, compared to stages I and II. Moreover, knockout (KO) and overexpression, as well as molecular and biochemical techniques, were used to investigate the biological functions of lncCDH5-3:3 in NSCLC cells, with a focus on the cells' proliferation and migration; (3) The finding that lncCDH5-3:3 silencing promotes apoptosis and probably regulates the cell cycle and E-cadherin expression in adenocarcinoma cell lines. In comparison, lncCDH5-3:3 overexpression increases the expression levels of proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers, such as EpCAM, Akt, and ERK1/2; however, at the same time, it also stimulates the expression of E-cadherin, which conversely inhibits the mobility capabilities of lung cancer cells; (4) The results of this study, which provide important insights into the role of lncRNAs in lung cancer. Our study shows that lncCDH5-3:3 affects important features of lung cancer cells, such as their viability and motility. The results support the idea that lncCDH5-3:3 is probably involved in the oncogenesis of NSCLC through the regulation of apoptosis and tumor cell metastasis formation.
Keywords: apoptosis; lncCDH5-3:3; migration; non-small cell lung cancer; proliferation; tumor cell aggressiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
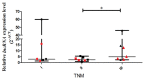
 ; the maximum values as
; the maximum values as  ; the median as —; and
; the median as —; and  represents the p-value from the post hoc test. The circles, squares, and triangles filled with the red color represent squamous cell carcinoma samples, while the black circles, squares, and triangles mark the adenocarcinoma samples.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test. The circles, squares, and triangles filled with the red color represent squamous cell carcinoma samples, while the black circles, squares, and triangles mark the adenocarcinoma samples.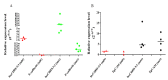
 ; the minimum values are marked as
; the minimum values are marked as  ; the medians are represented by circles, squares, and triangles;
; the medians are represented by circles, squares, and triangles;  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.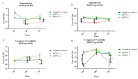
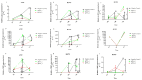
 ) and maximum (
) and maximum ( ) values from three biological replicates. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Friedman ANOVA and Dunn’s comparative post hoc tests. Statistically significant results are marked: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. In this figure, the medians are represented as circles, squares, and triangles, and
) values from three biological replicates. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Friedman ANOVA and Dunn’s comparative post hoc tests. Statistically significant results are marked: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. In this figure, the medians are represented as circles, squares, and triangles, and  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.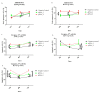
 ) and maximum (
) and maximum ( ) values from three biological replicates. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Friedman ANOVA and Dunn’s comparative post hoc tests. Statistically significant results are marked: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, and **** p < 0.0005. In this figure, the medians are represented by circles, squares, and triangles, and
) values from three biological replicates. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Friedman ANOVA and Dunn’s comparative post hoc tests. Statistically significant results are marked: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, and **** p < 0.0005. In this figure, the medians are represented by circles, squares, and triangles, and  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.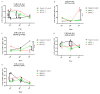
 ) and maximum (
) and maximum ( ) values from three biological replicates (n = 3). The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Friedman ANOVA and Dunn’s comparative post hoc tests. Statistically significant results are marked: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. Medians are marked as circles, squares, and triangles;
) values from three biological replicates (n = 3). The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Friedman ANOVA and Dunn’s comparative post hoc tests. Statistically significant results are marked: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. Medians are marked as circles, squares, and triangles;  represents the p-value from post hoc test.
represents the p-value from post hoc test.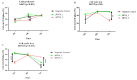
 ; the minimum values as
; the minimum values as  ; the medians as circles, squares, and triangles; and
; the medians as circles, squares, and triangles; and  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.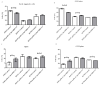
 ) and maximum (
) and maximum ( ) values from three biological replicates (n = 3). The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Wilcoxon test. Statistically significant results are marked as * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01;
) values from three biological replicates (n = 3). The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Wilcoxon test. Statistically significant results are marked as * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01;  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.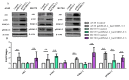
 ) and maximum (
) and maximum ( ) values of three independent replicates, and data are presented as fold changes relative to the control. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Wilcoxon test. Statistically significant results are marked as ** p < 0.01;
) values of three independent replicates, and data are presented as fold changes relative to the control. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Wilcoxon test. Statistically significant results are marked as ** p < 0.01;  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.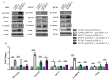
 ) and maximum (
) and maximum ( ) values of three independent replicates, and the data are presented as fold changes relative to the control. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Wilcoxon test. Statistically significant results are marked as * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01;
) values of three independent replicates, and the data are presented as fold changes relative to the control. The p-values were calculated on the basis of the Wilcoxon test. Statistically significant results are marked as * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01;  represents the p-value from the post hoc test.
represents the p-value from the post hoc test.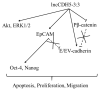
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits NSCLC cells proliferation and induces apoptosis by affecting p53 expression.BMC Cancer. 2013 Oct 7;13:461. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-461. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24098911 Free PMC article.
-
HOXC-AS2 mediates the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer by combining with HOXC13 gene.Cell Cycle. 2021 Jan;20(2):236-246. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1868161. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33427025 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA SNHG7 contributes to cell proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-449a/TGIF2 axis.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Feb;11(2):264-276. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13245. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31793741 Free PMC article.
-
The long non-coding RNA HNF1A-AS1 regulates proliferation and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):9160-72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3247. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25863539 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA PRNCR1 modulates non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and EMT through PRNCR1/miR-126-5p/MTDH axis.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20193153. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193153. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31912882 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

