The Protective Role of Celastrol in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Activating Nrf2/HO-1, PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways, Modulating NF-κb Signaling Pathways, and Inhibiting ERK Phosphorylation
- PMID: 35157199
- PMCID: PMC8881435
- DOI: 10.1007/s12013-022-01064-6
The Protective Role of Celastrol in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Activating Nrf2/HO-1, PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways, Modulating NF-κb Signaling Pathways, and Inhibiting ERK Phosphorylation
Abstract
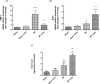
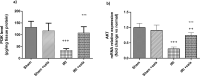
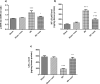
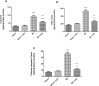
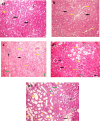
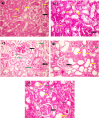
Celastrol, a natural triterpenoid derived from Tripterygium wilfordii, possesses numerous biological effects. We investigated celastrol's antioxidant potential through nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and its effect on phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathways, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) rat model. Rats were given celastrol 2 mg/kg orally for 1 week before subjection to renal ischemia-reperfusion surgery. Kidney functions, renal MDA, and reduced glutathione were determined; also, renal levels of ERK1/2, HO-1, PI3K, IL-6, TNF-α, IκBα, NF-κB/p65, and cleaved caspase-3 were measured. In addition, gene expression of kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), Nrf-2, and AKT were determined. Celastrol pretreatment attenuated oxidative stress and increased Nrf2 gene expression and HO-1 level. Also, it activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and decreased the p-ERK:t- ERK ratio and NFκBp65 level, with a remarkable decrease in inflammatory cytokines and cleaved caspase-3 levels compared with those in renal IRI rats. Conclusively, celastrol showed a reno-protective potential against renal IRI by suppressing oxidative stress through enhancing the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, augmenting cell survival PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, and reducing inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB activation.
Keywords: Celastrol; ERK phosphorylation; Nrf2/HO-1; PI3K/AKT; Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression by eckol, a phlorotannin compound, through activation of Erk and PI3K/Akt.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;42(2):297-305. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19931411
-
Targeting PI3K/p-Akt/eNOS, Nrf2/HO-1, and NF-κB/p53 signaling pathways by angiotensin 1-7 protects against liver injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Jan;42(1):e3938. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3938. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38269514
-
ATF3-mediated NRF2/HO-1 signaling regulates TLR4 innate immune responses in mouse liver ischemia/reperfusion injury.Am J Transplant. 2015 Jan;15(1):76-87. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12954. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Am J Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25359217
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting PI3K/Akt in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Alleviation: From Signaling Networks to Targeted Therapy.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7930-7949. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04039-1. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38441860 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Resveratrol Alleviation of Zearalenone-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in TM4 Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;14(11):733. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110733. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355983 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular network-based pharmacological study on the protective effect of Panax notoginseng rhizomes against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 18;14:1134408. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1134408. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37144215 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of SAV1 in Kidney Proximal Tubule Induces Maladaptive Repair after Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 23;25(9):4610. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094610. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731829 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Analysis of Ferroptosis-Related Genes and Its Implication in Drug Prediction against Fluorosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4221. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044221. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jannuzzi A, Kara M, Alpertunga B. Celastrol ameliorates acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Human & Experimental Toxicology. 2018;37(7):742–751. - PubMed
-
- Jung HW, Chung YS, Kim YS, Park YK. Celastrol inhibits production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines through MAPK signal transduction and NF-kappaB in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. Experimental & Molecular Medicine. 2007;39(6):715–721. - PubMed
-
- Joshi V, Venkatesha SH, Ramakrishnan C, Nanjaraj Urs AN, Hiremath V, Moudgil KD, et al. Celastrol modulates inflammation through inhibition of the catalytic activity of mediators of arachidonic acid pathway: Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA, 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2. Pharmacological Research. 2016;113(Pt A):265–275. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

