Roles of the Exosomes Derived From Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Tumor Immunity and Cancer Progression
- PMID: 35154134
- PMCID: PMC8829028
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.817942
Roles of the Exosomes Derived From Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Tumor Immunity and Cancer Progression
Abstract
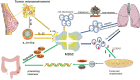
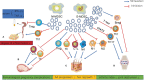
Tumor immunity is involved in malignant tumor progression. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) play an irreplaceable role in tumor immunity. MDSCs are composed of immature myeloid cells and exhibit obvious immunomodulatory functions. Exosomes released by MDSCs (MDSCs-Exos) have similar effects to parental MDSCs in regulating tumor immunity. In this review, we provided a comprehensive description of the characteristics, functions and mechanisms of exosomes. We analyzed the immunosuppressive, angiogenesis and metastatic effects of MDSCs-Exos in different tumors through multiple perspectives. Immunotherapy targeting MDSCs-Exos has demonstrated great potential in cancers and non-cancerous diseases.
Keywords: cancer; exosome; immune escape; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; tumor immunity.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Yuan, Hu, Yuan and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-derived exosomes, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and tumor microenvironment.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Aug 22;12(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0772-z. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31438991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expansion and functions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Lett. 2016 Sep 28;380(1):253-6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.022. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26519756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The New Era of Cancer Immunotherapy: Targeting Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells to Overcome Immune Evasion.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 30;11:1680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01680. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunosuppressive Effects of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer and Immunotherapy.Cells. 2021 May 11;10(5):1170. doi: 10.3390/cells10051170. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34065010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Oct 7;6(1):362. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00670-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34620838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal Communication Between the Tumor Microenvironment and Innate Immunity and Its Therapeutic Application.Immune Netw. 2022 Sep 26;22(5):e38. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e38. eCollection 2022 Oct. Immune Netw. 2022. PMID: 36381957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumorigenic and tumoricidal properties of exosomes in cancers; a forward look.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 15;22(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01510-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38360641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid‑derived suppressor cells: Key immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Sep;65(3):85. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5673. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39054950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Exosomes in Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 21;14(16):4036. doi: 10.3390/cancers14164036. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The rising roles of exosomes in the tumor microenvironment reprogramming and cancer immunotherapy.MedComm (2020). 2024 Apr 7;5(4):e541. doi: 10.1002/mco2.541. eCollection 2024 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38585234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao Y, Shao Q, Zhu H, Xu H, Long W, Yu B, et al. . Resveratrol Ameliorates Lewis Lung Carcinoma-Bearing Mice Development, Decreases Granulocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Accumulation and Impairs Its Suppressive Ability. Cancer Sci (2018) 109(9):2677–86. doi: 10.1111/cas.13720 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

