Central nervous system tumors in children under 5 years of age: a report on treatment burden, survival and long-term outcomes
- PMID: 35147892
- PMCID: PMC9021074
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-022-03963-3
Central nervous system tumors in children under 5 years of age: a report on treatment burden, survival and long-term outcomes
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Central nervous system tumors in children under 5 years of age: a report on treatment burden, survival and long-term outcomes.J Neurooncol. 2022 Apr;157(2):319. doi: 10.1007/s11060-022-03976-y. J Neurooncol. 2022. PMID: 35226242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: The challenges of treating central nervous system (CNS) tumors in young children are many. These include age-specific tumor characteristics, limited treatment options, and susceptibility of the developing CNS to cytotoxic therapy. The aim of this study was to analyze the long-term survival, health-related, and educational/occupational outcomes of this vulnerable patient population.
Methods: Retrospective study of 128 children diagnosed with a CNS tumor under 5 years of age at a single center in Switzerland between 1990 and 2019.
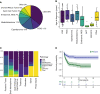
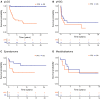
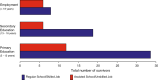
Results: Median age at diagnosis was 1.81 years [IQR, 0.98-3.17]. Median follow-up time of surviving patients was 8.39 years [range, 0.74-23.65]. The main tumor subtypes were pediatric low-grade glioma (36%), pediatric high-grade glioma (11%), ependymoma (16%), medulloblastoma (11%), other embryonal tumors (7%), germ cell tumors (3%), choroid plexus tumors (6%), and others (9%). The 5-year overall survival (OS) was 78.8% (95% CI, 71.8-86.4%) for the whole cohort. Eighty-seven percent of survivors > 5 years had any tumor- or treatment-related sequelae with 61% neurological complications, 30% endocrine sequelae, 17% hearing impairment, and 56% visual impairment at last follow-up. Most patients (72%) attended regular school or worked in a skilled job at last follow-up.
Conclusion: Young children diagnosed with a CNS tumor experience a range of complications after treatment, many of which are long-lasting and potentially debilitating. Our findings highlight the vulnerabilities of this population, the need for long-term support and strategies for rehabilitation, specifically tailored for young children.
Keywords: Brain tumors; Educational/occupational outcomes; Long-term outcome; Pediatrics; Survival.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Topical and oral steroids for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Dec 13;12(12):CD015255. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015255.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38088821 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 6;2013(6):CD008933. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008933.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23744561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disease burden and healthcare utilization in pediatric low-grade glioma: A United States retrospective study of linked claims and electronic health records.Neurooncol Pract. 2024 Apr 27;11(5):583-592. doi: 10.1093/nop/npae037. eCollection 2024 Oct. Neurooncol Pract. 2024. PMID: 39279771 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Optic Pathway Gliomas Resource Utilization and Prevalence in the OptumLabs Data Warehouse.J Neuroophthalmol. 2024 Mar 1;44(1):10-15. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001960. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Neuroophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37505911 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical factors, management, and outcomes of children under 3 years old with central nervous system tumors: single-center experience.Childs Nerv Syst. 2024 Aug;40(8):2311-2320. doi: 10.1007/s00381-024-06386-9. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Childs Nerv Syst. 2024. PMID: 38619586
-
Geographic and temporal trends in pediatric and young adult brain tumors in Kentucky, 1995-2019.Cancer Epidemiol. 2024 Feb;88:102499. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2023.102499. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38056245 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments associated with all-cause mortality among children with primary brain and central nervous system tumors: a retrospective cohort study from the SEER database.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Aug 30;12(8):1504-1516. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-362. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37692544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Capper D, Jones DTW, Sill M, Hovestadt V, Schrimpf D, Sturm D, Koelsche C, Sahm F, Chavez L, Reuss DE, Kratz A, Wefers AK, Huang K, Pajtler KW, Schweizer L, Stichel D, Olar A, Engel NW, Lindenberg K, Harter PN, Braczynski AK, Plate KH, Dohmen H, Garvalov BK, Coras R, Hölsken A, Hewer E, Bewerunge-Hudler M, Schick M, Fischer R, Beschorner R, Schittenhelm J, Staszewski O, Wani K, Varlet P, Pages M, Temming P, Lohmann D, Selt F, Witt H, Milde T, Witt O, Aronica E, Giangaspero F, Rushing E, Scheurlen W, Geisenberger C, Rodriguez FJ, Becker A, Preusser M, Haberler C, Bjerkvig R, Cryan J, Farrell M, Deckert M, Hench J, Frank S, Serrano J, Kannan K, Tsirigos A, Brück W, Hofer S, Brehmer S, Seiz-Rosenhagen M, Hänggi D, Hans V, Rozsnoki S, Hansford JR, Kohlhof P, Kristensen BW, Lechner M, Lopes B, Mawrin C, Ketter R, Kulozik A, Khatib Z, Heppner F, Koch A, Jouvet A, Keohane C, Mühleisen H, Mueller W, Pohl U, Prinz M, Benner A, Zapatka M, Gottardo NG, Driever PH, Kramm CM, Müller HL, Rutkowski S, von Hoff K, Frühwald MC, Gnekow A, Fleischhack G, Tippelt S, Calaminus G, Monoranu CM, Perry A, Jones C, Jacques TS, Radlwimmer B, Gessi M, Pietsch T, Schramm J, Schackert G, Westphal M, Reifenberger G, Wesseling P, Weller M, Collins VP, Blümcke I, Bendszus M, Debus J, Huang A, Jabado N, Northcott PA, Paulus W, Gajjar A, Robinson GW, Taylor MD, Jaunmuktane Z, Ryzhova M, Platten M, Unterberg A, Wick W, Karajannis MA, Mittelbronn M, Acker T, Hartmann C, Aldape K, Schüller U, Buslei R, Lichter P, Kool M, Herold-Mende C, Ellison DW, Hasselblatt M, Snuderl M, Brandner S, Korshunov A, von Deimling A, Pfister SM. DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours. Nature. 2018;555:469–474. doi: 10.1038/nature26000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnson KJ, Cullen J, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Ostrom QT, Langer CE, Turner MC, McKean-Cowdin R, Fisher JL, Lupo PJ, Partap S, Schwartzbaum JA, Scheurer ME. Childhood brain tumor epidemiology: a brain tumor epidemiology consortium review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2014;23:2716–2736. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0207. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

