Human transcription factor protein interaction networks
- PMID: 35140242
- PMCID: PMC8828895
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28341-5
Human transcription factor protein interaction networks
Abstract
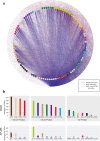
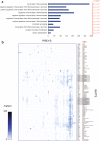
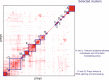
Transcription factors (TFs) interact with several other proteins in the process of transcriptional regulation. Here, we identify 6703 and 1536 protein-protein interactions for 109 different human TFs through proximity-dependent biotinylation (BioID) and affinity purification mass spectrometry (AP-MS), respectively. The BioID analysis identifies more high-confidence interactions, highlighting the transient and dynamic nature of many of the TF interactions. By performing clustering and correlation analyses, we identify subgroups of TFs associated with specific biological functions, such as RNA splicing or chromatin remodeling. We also observe 202 TF-TF interactions, of which 118 are interactions with nuclear factor 1 (NFI) family members, indicating uncharacterized cross-talk between NFI signaling and other TF signaling pathways. Moreover, TF interactions with basal transcription machinery are mainly observed through TFIID and SAGA complexes. This study provides a rich resource of human TF interactions and also act as a starting point for future studies aimed at understanding TF-mediated transcription.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteomic analyses reveal distinct chromatin-associated and soluble transcription factor complexes.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Jan 21;11(1):775. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145504. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 25609649 Free PMC article.
-
Proximity biotinylation and affinity purification are complementary approaches for the interactome mapping of chromatin-associated protein complexes.J Proteomics. 2015 Apr 6;118:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25281560 Free PMC article.
-
Combined proximity labeling and affinity purification-mass spectrometry workflow for mapping and visualizing protein interaction networks.Nat Protoc. 2020 Oct;15(10):3182-3211. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-0365-x. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32778839
-
Transcription factors: Bridge between cell signaling and gene regulation.Proteomics. 2021 Dec;21(23-24):e2000034. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202000034. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34314098 Review.
-
Transcription factor interactions in genomic nuclear receptor function.Epigenomics. 2011 Aug;3(4):471-85. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.66. Epigenomics. 2011. PMID: 22126206 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of omics technologies in studies on antitumor effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine.Chin Med. 2024 Sep 9;19(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00995-x. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39252074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid profiling of transcription factor-cofactor interaction networks reveals principles of epigenetic regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 23;52(17):10276-10296. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae706. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39166482 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter Methylation Leads to Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4A Loss and Pancreatic Cancer Aggressiveness.Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 Apr 24;3(5):687-702. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.04.005. eCollection 2024. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024. PMID: 39165427 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Proximity-Dependent Protein Labeling (BioID2) for Protein Interaction Mapping in E. coli.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2828:87-106. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4023-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39147973
References
-
- Babu MM, Luscombe NM, Aravind L, Gerstein M, Teichmann SA. Structure and evolution of transcriptional regulatory networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004;14:283–291. - PubMed
-
- Vaquerizas JM, Kummerfeld SK, Teichmann SA, Luscombe NM. A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009;10:252–263. - PubMed
-
- Lambert SA, et al. The human transcription factors. Cell. 2018;172:650–665. - PubMed
-
- Brivanlou AH, Darnell JE., Jr. Signal transduction and the control of gene expression. Science. 2002;295:813–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

