Downregulation of NCL attenuates tumor formation and growth in HeLa cells by targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 35128835
- PMCID: PMC8921942
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4569
Downregulation of NCL attenuates tumor formation and growth in HeLa cells by targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
Background: Nucleolin (NCL, C23) is a multifunctional phosphoprotein that plays a vital role in modulating the survival, proliferationand apoptosis of cancer cells. However, the effects of NCL on cervical cancer and the underlying mechanisms behind this are poorly understood.
Methods: Lentiviral transfection technology was used to construct NCL knockdown cell lines. MTT, colony formation assays, and tumorigenic assays in vivo were performed to observe cell proliferation. HOECHST 33342 staining, flow cytometry, and caspase activity assay were used to test cell apoptosis. RNA-Seq, Western blotting, and RT-PCR were conducted to investigate the specific molecular mechanism.
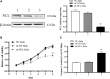
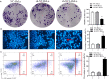
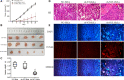
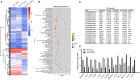
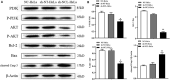
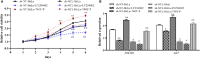
Results: NCL knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis both in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistic studies revealed that NCL knockdown inhibited the PI3K/AKT pathway by upregulating FGF, ITGA, TNXB, VEGF, Caspase 3, and Bax, as well as by downregulating AKT, GNB4, CDK6, IL6R, LAMA, PDGFD, PPP2RSA and BCL-2. In addition, the expression levels of apoptosis-related genes after using a PI3K inhibitor LY294002 were consistent with shRNA studies, while treatment with a 740Y-P agonist showed the opposite effect.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that downregulation of NCL may be a novel treatment strategy forcervical cancer.
Keywords: HeLa cells; PI3K/AKT pathway; RNA-Seq; apoptosis; molecular mechanism; nucleolin.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing UHRF1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Promotes Cell Apoptosis in Retinoblastoma Via the PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Apr;26(2):1079-1088. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00656-7. Epub 2019 May 2. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31044388
-
Curcumol inhibits breast cancer growth via NCL/ERα36 and the PI3K/AKT pathway.Food Funct. 2023 Jan 23;14(2):874-885. doi: 10.1039/d2fo02387c. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 36537297
-
Regulation of cell apoptosis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer through PI3K/Akt pathway via Polo-like kinase 1.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):49-56. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4820. Epub 2016 May 18. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27220401 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of TBRG4 suppresses proliferation, invasion and promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by downregulating TGF-β1 expression and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jun 15;686:108351. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108351. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32240636
-
COL3A1-positive endothelial cells influence LUAD prognosis and regulate LUAD carcinogenesis by NCL-PI3K-AKT axis.J Gene Med. 2024 Jan;26(1):e3573. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3573. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Gene Med. 2024. PMID: 37547956
Cited by
-
Tissue-resident memory T cell signatures from single-cell analysis associated with better melanoma prognosis.iScience. 2024 Feb 20;27(3):109277. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109277. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38455971 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-based comparison of CD4+ T cell DNA methylation in lupus reveals proinflammatory epigenetic changes in men.Clin Immunol. 2022 Oct;243:109116. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109116. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36075396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng HR, Chen J. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of early stage cervical cancer in young patients. J Mod Oncol. 2016;24:24678‐24680.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

