Current understanding of the role of tyrosine kinase 2 signaling in immune responses
- PMID: 35126866
- PMCID: PMC8790287
- DOI: 10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.1
Current understanding of the role of tyrosine kinase 2 signaling in immune responses
Abstract
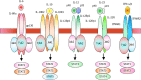
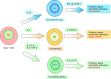
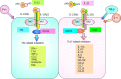
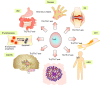
Immune system is a complex network that clears pathogens, toxic substrates, and cancer cells. Distinguishing self-antigens from non-self-antigens is critical for the immune cell-mediated response against foreign antigens. The innate immune system elicits an early-phase response to various stimuli, whereas the adaptive immune response is tailored to previously encountered antigens. During immune responses, B cells differentiate into antibody-secreting cells, while naïve T cells differentiate into functionally specific effector cells [T helper 1 (Th1), Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cells]. However, enhanced or prolonged immune responses can result in autoimmune disorders, which are characterized by lymphocyte-mediated immune responses against self-antigens. Signal transduction of cytokines, which regulate the inflammatory cascades, is dependent on the members of the Janus family of protein kinases. Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2) is associated with receptor subunits of immune-related cytokines, such as type I interferon, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-23. Clinical studies on the therapeutic effects and the underlying mechanisms of Tyk2 inhibitors in autoimmune or chronic inflammatory diseases are currently ongoing. This review summarizes the findings of studies examining the role of Tyk2 in immune and/or inflammatory responses using Tyk2-deficient cells and mice.
Keywords: Cytokines; Immune system; Inflammation; Signal transduction; Tyrosine kinase 2.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Advantage of Tyk2 Inhibition for Treating Autoimmune and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(11):1585-1592. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-00609. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 34719635 Review.
-
Tyk2 negatively regulates adaptive Th1 immunity by mediating IL-10 signaling and promoting IFN-gamma-dependent IL-10 reactivation.J Immunol. 2006 Jun 15;176(12):7263-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7263. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16751369
-
The effector T helper cell triade.Riv Biol. 2009 Jan-Apr;102(1):61-74. Riv Biol. 2009. PMID: 19718623 Review.
-
Tyrosine kinase 2 plays critical roles in the pathogenic CD4 T cell responses for the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 1;183(11):7539-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902740. Epub 2009 Nov 16. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19917699
-
The TYK2-P1104A Autoimmune Protective Variant Limits Coordinate Signals Required to Generate Specialized T Cell Subsets.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 25;10:44. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00044. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30740104 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Pipeline of Novel Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease; State of the Art Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 1;11(3):747. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030747. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting the JAK/STAT Pathway in Psoriasis: Focus on TYK2 Inhibition.J Clin Med. 2024 May 24;13(11):3091. doi: 10.3390/jcm13113091. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38892802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin as a possible complementary therapy in multiple sclerosis: Anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and remyelination potential properties.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 29;9(11):e21741. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21741. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37954351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular heterogeneity in disease severity and clinical outcome: Granular understanding of immune response is key.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 22;13:973070. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.973070. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36072602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Associations with Coronavirus Susceptibility and Disease Severity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1412:119-140. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-28012-2_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37378764 Review.
References
-
- O'Shea JJ, Ma A, Lipsky P. Cytokines and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Ihle JN. Cytokine receptor signalling. Nature. 1995;377:591–594. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE. STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Rodig SJ, Meraz MA, White JM, Lampe PA, Riley JK, Arthur CD, King KL, Sheehan KC, Yin L, Pennica D, Johnson EM Jr, Schreiber RD. Disruption of the Jak1 gene demonstrates obligatory and nonredundant roles of the Jaks in cytokine-induced biologic responses. Cell. 1998;93:373–383. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

