Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome: Identification of Novel Variants in the Genes HPS3, HPS5, and DTNBP1 (HPS-7)
- PMID: 35126127
- PMCID: PMC8807545
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.786937
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome: Identification of Novel Variants in the Genes HPS3, HPS5, and DTNBP1 (HPS-7)
Abstract
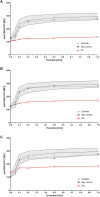
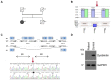
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS), a rare heterogeneous autosomal recessive disorder, is characterized by oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) and a bleeding diathesis due to a defect regarding melanosomes and platelet delta (δ)-granule secretion. Interestingly, patients with HPS type 2 (HPS-2) or HPS type 10 (HPS-10) present additionally with an immunological defect. We investigated three patients (IP1, IP2, and IP3) who suffer from a bleeding diathesis. Platelet aggregometry showed impaired platelet function and flow cytometry revealed a severely reduced platelet CD63 expression hinting to either a defect of platelet delta granule secretion or a decreased number of delta granules in these patients. However, only IP3 presents with an apparent OCA. We performed panel sequencing and identified a homozygous deletion of exon 6 in DTNBP1 for IP3. Western analysis confirmed the absence of the encoded protein dysbindin confirming the diagnosis of HPS-7. Interestingly, this patient reported additionally recurrent bacterial infections. Analysis of lymphocyte cytotoxicity showed a slightly reduced NK-degranulation previously documented in a more severe form in patients with HPS-2 or HPS-10. IP1 is carrier of two compound heterozygous variants in the HPS3 gene (c.65C > G and c.1193G > A). A homozygous variant in HPS5 (c.760G > T) was identified in IP2. The novel missense variants were classified as VUS (variant of uncertain significance) according to ACMG guidelines. For IP1 with the compound heterozygous variants in HPS3 a specialized ophthalmological examination showed ocular albinism. HPS3 and HPS5 encode subunits of the BLOC-2 complex and patients with HPS-3 or HPS-5 are known to present with variable/mild hypopigmentation.
Keywords: BLOC-1; BLOC-2; HPS-3; HPS-5; HPS-7; Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS).
Copyright © 2022 Boeckelmann, Wolter, Neubauer, Sobotta, Lenz, Glonnegger, Käsmann-Kellner, Mann, Ehl and Zieger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel variant in HPS3 gene in a patient with Hermansky Pudlak syndrome (HPS) type 3.Platelets. 2020 Oct 2;31(7):960-963. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2019.1704716. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Platelets. 2020. PMID: 31880485
-
Novel mutation in two brothers with Hermansky Pudlak syndrome type 3.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2017 Sep;67:75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28284561
-
Oculocutaneous albinism and bleeding diathesis due to a novel deletion in the HPS3 gene.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 15;13:936064. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.936064. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36046236 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Likely Pathogenic Variant in the BLOC1S5 Gene Associated with Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome Type 11 and an Overview of Human BLOC-1 Deficiencies.Cells. 2021 Oct 1;10(10):2630. doi: 10.3390/cells10102630. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 7: a case report and comprehensive literature review on the identification of DTNBP1 variants.Ophthalmic Genet. 2024 Jun;45(3):262-266. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2023.2291670. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Ophthalmic Genet. 2024. PMID: 38097925 Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput microfluidic blood testing to phenotype genetically linked platelet disorders: an aid to diagnosis.Blood Adv. 2023 Oct 24;7(20):6163-6177. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023009860. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 37389831 Free PMC article.
-
Masks of Albinism: Clinical Spectrum of Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11260. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011260. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457042 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel GATA1 Variant in the C-Terminal Zinc Finger Compared with the Platelet Phenotype of Patients with A Likely Pathogenic Variant in the N-Terminal Zinc Finger.Cells. 2022 Oct 14;11(20):3223. doi: 10.3390/cells11203223. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291092 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Selection Sweep Analysis to Identify Candidate Genes with Black and Brown Color in Tibetan Sibu Yaks.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 24;14(17):2458. doi: 10.3390/ani14172458. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272243 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

