Bioenzyme-based nanomedicines for enhanced cancer therapy
- PMID: 35119544
- PMCID: PMC8816986
- DOI: 10.1186/s40580-022-00297-8
Bioenzyme-based nanomedicines for enhanced cancer therapy
Abstract
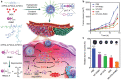
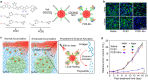
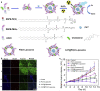
Bioenzymes that catalyze reactions within living systems show a great promise for cancer therapy, particularly when they are integrated with nanoparticles to improve their accumulation into tumor sites. Nanomedicines can deliver toxic bioenzymes into cancer cells to directly cause their death for cancer treatment. By modulating the tumor microenvironment, such as pH, glucose concentration, hypoxia, redox levels and heat shock protein expression, bioenzyme-based nanomedicines play crucial roles in improving the therapeutic efficacy of treatments. Moreover, bioenzyme-mediated degradation of the major components in tumor extracellular matrix greatly increases the penetration and retention of nanoparticles in deep tumors and infiltration of immune cells into tumor tissues, thus enhancing the efficacies of chemotherapy, phototherapy and immunotherapy. In this review, we summarize the recent progresses of bioenzyme-based nanomedicines for enhanced cancer therapy. The design and working mechanisms of the bioenzyme-based nanomedicines to achieve enhanced chemotherapy, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, chemodynamic therapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy are introduced in detail. At the end of this review, a conclusion and current challenges and perspectives in this field are given.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Drug delivery system; Enzyme; Nanomedicine; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tumor extracellular matrix modulating strategies for enhanced antitumor therapy of nanomedicines.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Jul 15;16:100364. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100364. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35875197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Targeted Nanomedicine for Immunotherapy.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Dec 15;53(12):2765-2776. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00518. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 33161717 Review.
-
Recent advances in dual- and multi-responsive nanomedicines for precision cancer therapy.Biomaterials. 2022 Dec;291:121906. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121906. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 36395660 Review.
-
Nanomedicine-based multimodal therapies: Recent progress and perspectives in colon cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jan 28;29(4):670-681. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i4.670. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36742173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-infrared absorbing semiconducting polymer nanomedicines for cancer therapy.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023 May-Jun;15(3):e1865. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1865. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36284504 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-loaded hydrogels for photothermal therapy of cancer cells.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 16;11:1130523. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1130523. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37008029 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on Stimulus-Responsive Polymer Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 11;15(7):1928. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071928. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor extracellular matrix modulating strategies for enhanced antitumor therapy of nanomedicines.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Jul 15;16:100364. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100364. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35875197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoformulations-Based Metronomic Chemotherapy: Mechanism, Challenges, Recent Advances, and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 8;15(4):1192. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041192. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomaterial-Based Responsive Nanomedicines for Targeting Solid Tumor Microenvironments.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 26;16(2):179. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020179. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jin S, Weng L, Li Z, Yang Z, Zhu L, Shi J, Tang W, Ma W, Zong H, Jiang W. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2020;8:4620–4626. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Wang M, Ying H, Su D, Zhang H, Lu G, Chen J. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018;4:2404–2411. - PubMed
-
- Si X, Song W, Yang S, Ma L, Yang C, Tang Z. Macromol. Biosci. 2019;19:1900148. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
