The prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at different time points in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving liver resection
- PMID: 35117389
- PMCID: PMC8798615
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr.2019.11.29
The prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at different time points in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving liver resection
Abstract
Background: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been demonstrated a significant association with the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The current study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of NLR at different time points in HCC patients receiving liver resection.
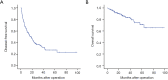
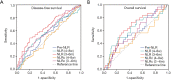
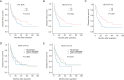
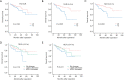
Methods: Data were retrospectively collected from 195 HCC patients receiving liver resection. The preoperative NLR (pre-NLR), postoperative NLR (post-NLR) and corresponding changes of NLR (NLRc) at different time points were calculated. The disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) was calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test. Both univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to evaluate their prognostic values for DFS and OS. And the prognostic significance of pre-NLR, post-NLRs, and NLRcs were further evaluated with subgroup analysis and with early and late recurrence of HCC.
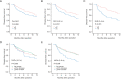
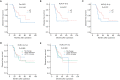
Results: Pre-NLR was not significantly correlated with DFS or OS (both P>0.05), whereas higher post-NLR at 4-8 weeks [NLR (4-8 w)] and 3-6 months [(NLR (3-6 m)] predicted worse DFS (P=0.023 and P<0.001, respectively) and OS (P=0.012 and P=0.001, respectively). The value of area under the curve (AUC) of NLR (3-6 m) were higher than NLR (4-8 w) for DFS (0.656 vs. 0.572) and OS (0.650 vs. 0.621). Multivariate analyses showed that NLRc (4-8 w) was not a significant predictor of DFS (P=0.369) or OS (P=0.173), while the NLRc (3-6 m) with 25% increase was found to be an independent factor for adverse DFS in patients with HCC (P=0.041). The AUC of NLRc (3-6 m) for DFS was 0.600. Subgroup analysis showed NLR (3-6 m) was significantly corrected to DFS (P<0.001) and OS (P=0.001) in patients with cirrhosis. And NLR (3-6 m) also showed with significant correlation with early recurrence (P<0.001), while NLR (4-8 w) was found with significant association both with early and late recurrence (P=0.037 and P=0.027, respectively).
Conclusions: The post-NLRs are significant predictors of clinical outcome in HCC patients receiving liver resection, and post-NLR and NLRc with a relatively long-term interval after operation have better prognostic values.
Keywords: Disease-free survival (DFS); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR); overall survival (OS); prognosis.
2020 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2019.11.29). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of preoperative aspartate aminotransferase to neutrophil ratio index in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):72276-72289. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10848. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27472390 Free PMC article.
-
A novel and accurate predictor of survival for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) combined with the aspartate aminotransferase/platelet count ratio index (APRI).BMC Cancer. 2016 Feb 22;16:137. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2189-1. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26907597 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative inflammatory markers as prognostic predictors after hepatocellular carcinoma resection: data from a western referral center.BMC Surg. 2022 Sep 2;22(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01779-6. BMC Surg. 2022. PMID: 36056350 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Predictors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Various Treatments: a Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):967-981. doi: 10.1159/000485396. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29179180 Review.
-
The prognostic significance of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving hepatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2018 Jul;55:73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.05.022. Epub 2018 May 19. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29787804 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical value of combined preoperative-postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis after radiofrequency ablation.Br J Radiol. 2023 Apr 1;96(1145):20220887. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220887. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36715151 Free PMC article.
-
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a new prognostic factor in cancers: a narrative review.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 4;13:1228076. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1228076. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37860198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Changes in the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predict the Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 May 14;12:3433-3444. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S245396. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32523374 Free PMC article.
-
Significant association between high neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1211399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1211399. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809083 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
