Maladaptive functional changes in alveolar fibroblasts due to perinatal hyperoxia impair epithelial differentiation
- PMID: 35113810
- PMCID: PMC8983125
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.152404
Maladaptive functional changes in alveolar fibroblasts due to perinatal hyperoxia impair epithelial differentiation
Abstract
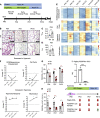
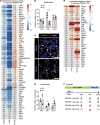
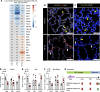
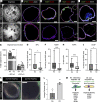
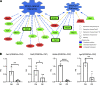
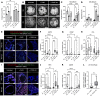
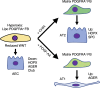
Infants born prematurely worldwide have up to a 50% chance of developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), a clinical morbidity characterized by dysregulated lung alveolarization and microvascular development. It is known that PDGFR alpha-positive (PDGFRA+) fibroblasts are critical for alveolarization and that PDGFRA+ fibroblasts are reduced in BPD. A better understanding of fibroblast heterogeneity and functional activation status during pathogenesis is required to develop mesenchymal population-targeted therapies for BPD. In this study, we utilized a neonatal hyperoxia mouse model (90% O2 postnatal days 0-7, PN0-PN7) and performed studies on sorted PDGFRA+ cells during injury and room air recovery. After hyperoxia injury, PDGFRA+ matrix and myofibroblasts decreased and PDGFRA+ lipofibroblasts increased by transcriptional signature and population size. PDGFRA+ matrix and myofibroblasts recovered during repair (PN10). After 7 days of in vivo hyperoxia, PDGFRA+ sorted fibroblasts had reduced contractility in vitro, reflecting loss of myofibroblast commitment. Organoids made with PN7 PDGFRA+ fibroblasts from hyperoxia in mice exhibited reduced alveolar type 1 cell differentiation, suggesting reduced alveolar niche-supporting PDGFRA+ matrix fibroblast function. Pathway analysis predicted reduced WNT signaling in hyperoxia fibroblasts. In alveolar organoids from hyperoxia-exposed fibroblasts, WNT activation by CHIR increased the size and number of alveolar organoids and enhanced alveolar type 2 cell differentiation.
Keywords: Development; Fibrosis; Growth factors; Mouse models; Pulmonology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prenatal FGFR2 Signaling via PI3K/AKT Specifies the PDGFRA+ Myofibroblast.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;70(1):63-77. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0245OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37734036 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Regulation of GH-IGF1 Signaling in Injury and Recovery in Hyperoxia-Induced Neonatal Lung Injury.Cells. 2021 Oct 29;10(11):2947. doi: 10.3390/cells10112947. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831169 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal periostin knockout mice are protected from hyperoxia-induced alveolar simplication.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031336. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363622 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting p16INK4a Promotes Lipofibroblasts and Alveolar Regeneration after Early-Life Injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Oct 15;202(8):1088-1104. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1573OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32628504
-
Resident interstitial lung fibroblasts and their role in alveolar stem cell niche development, homeostasis, injury, and regeneration.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):1021-1032. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0526. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33624948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Pdgfra fibroblast heterogeneity in normal and fibrotic mouse lung.JCI Insight. 2023 Nov 22;8(22):e164380. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.164380. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37824216 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal FGFR2 Signaling via PI3K/AKT Specifies the PDGFRA+ Myofibroblast.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;70(1):63-77. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0245OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37734036 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL10 deficiency limits macrophage infiltration, preserves lung matrix, and enables lung growth in bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Inflamm Regen. 2023 Oct 24;43(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s41232-023-00301-6. Inflamm Regen. 2023. PMID: 37876024 Free PMC article.
-
Open questions in human lung organoid research.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 13;13:1083017. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1083017. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36712670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic analysis reveals the relationship between macrophage infiltration and Cybb downregulation in hyperoxia-induced bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 29;14(1):20089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70877-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39209930 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

