Involvement of the BDNF-TrkB-KCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain after brachial plexus avulsion
- PMID: 35106976
- PMCID: PMC8933754
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2464
Involvement of the BDNF-TrkB-KCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain after brachial plexus avulsion
Abstract
Introduction: Brachial plexus avulsion significantly increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) release in the spinal cord. Here we investigated the involvement of the BDNF-TrkB-KCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain caused by BPA injury. We hypothesized that activation of BDNF-TrkB may inhibit neuronal excitability by downregulating KCC2 to maintain a high intracellular Cl-concentration. We established a neuropathic pain rat model by avulsion of the lower trunk brachial plexus, and investigated the effects of the TrkB-specific antibody K-252a on the expression of BDNF, TrkB, and KCC2.
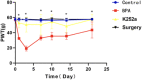
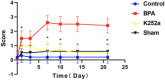
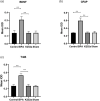
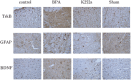
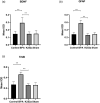
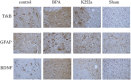
Methods: We randomly divided 40 male SD rats into four groups. In the brachial plexus avulsion group, C8-T1 roots were avulsed from the spinal cord at the lower trunk level. In the K252a group, 5uL K252a was applied intrathecally daily for three days after avulsion. In the sham surgery group, expose only and without damage. The control group did not undergo any treatment. Mechanical hyperalgesia and cold allodynia were analyzed by electronic pain measuring instrument and acetone spray method at different time points on days 1, 3, 7, 10, 14, and 21 after surgery. At 21 days after surgery, the expression of BDNF and TrkB in dorsal horn neurons and GFAP in astrocytes were detected by immunohistochemistry at the C5-T1 segment of the spinal cord. The expression levels of BDNF, TrkB, and KCC2 in the C5-T1 spinal cord were measured by Western Blot at 7 and 21 days.
Results: Mechanical hyperalgesia and cold allodynia were significantly reduced in the K252a group compared with the brachial plexus avulsion group. Compared with the BPA group, BDNF, TrkB and GFAP were significantly decreased in the K252a group at 21 days after treatment by immunohistochemical test. In the WB test, the expressions of BDNF and TrkB in the K252a group were quantitatively detected to be decreased, while the expression of KCC2 was increased, which was obvious at 7 and 21 days.
Conclusion: BDNF-TrkB-KCC2 pathway can significantly relieve neuropathic pain after BPA, and is a potential target for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Keywords: BDNF; K252a; KCC2; TrkB; brachial plexus avulsion; neuropathic pain.
© 2022 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Generally Administered Anti-Nerve Growth Factor Receptor (p75NTR) Antibody on Pain-Related Behavior, Dorsal Root Ganglia, and Spinal Glia Activation in a Rat Model of Brachial Plexus Avulsion.J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Oct;40(10):2017-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Aug 29. J Hand Surg Am. 2015. PMID: 26321458
-
Trifluoro-icaritin ameliorates spared nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain by inhibiting microglial activation through α7nAChR-mediated blockade of BDNF/TrkB/KCC2 signaling in the spinal cord of rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jan;157:114001. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114001. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36375307
-
Evaluation of Neuropathic Pain in a Rat Model of Total Brachial Plexus Avulsion from Behavior to Brain Metabolism.Pain Physician. 2019 May;22(3):E215-E224. Pain Physician. 2019. PMID: 31151344
-
Role of the BDNF-TrkB pathway in KCC2 regulation and rehabilitation following neuronal injury: A mini review.Neurochem Int. 2019 Sep;128:32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Neurochem Int. 2019. PMID: 30986502 Review.
-
BDNF in Neuropathic Pain; the Culprit that Cannot be Apprehended.Neuroscience. 2024 Apr 5;543:49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.02.020. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Neuroscience. 2024. PMID: 38417539 Review.
Cited by
-
Treadmill running on neuropathic pain: via modulation of neuroinflammation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jun 26;17:1345864. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1345864. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38989156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF as a biomarker for neuropathic pain: Consideration of mechanisms of action and associated measurement challenges.Brain Behav. 2023 Mar;13(3):e2903. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2903. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36722793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves cognitive impairments in mice with sepsis.PeerJ. 2024 May 28;12:e17427. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17427. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38827289 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic Plasticity: Common Mechanistic Underpinnings of Pathology in Spinal Cord Injury and the Brain.Cells. 2022 Sep 17;11(18):2910. doi: 10.3390/cells11182910. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Nociception, and Pain.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 30;14(5):539. doi: 10.3390/biom14050539. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baron, R. , Binder, A. , & Wasner, G. (2010). Neuropathic pain: Diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurology, 9(8), 807–819. - PubMed
-
- Breivik, H. , Collett, B. , Ventafridda, V. , Cohen, R. , & Gallacher, D. (2006). Survey of chronic pain in Europe: Prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. European Journal of Pain, 10(4), 287–333. - PubMed
-
- Buck, H. , & Winter, J. (1996). K252a modulates the expression of nerve growth factor‐dependent capsaicin sensitivity and substance P levels in cultured adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. Journal of Neurochemistry, 67(1), 345–351. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

