Mitochondria homeostasis: Biology and involvement in hepatic steatosis to NASH
- PMID: 35105958
- PMCID: PMC9061859
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-00864-z
Mitochondria homeostasis: Biology and involvement in hepatic steatosis to NASH
Abstract
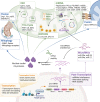
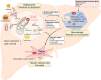
Mitochondrial biology and behavior are central to the physiology of liver. Multiple mitochondrial quality control mechanisms remodel mitochondrial homeostasis under physiological and pathological conditions. Mitochondrial dysfunction and damage induced by overnutrition lead to oxidative stress, inflammation, liver cell death, and collagen production, which advance hepatic steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Accumulating evidence suggests that specific interventions that target mitochondrial homeostasis, including energy metabolism, antioxidant effects, and mitochondrial quality control, have emerged as promising strategies for NASH treatment. However, clinical translation of these findings is challenging due to the complex and unclear mechanisms of mitochondrial homeostasis in the pathophysiology of NASH.
Keywords: NASH; liver; metabolism; mitochondria; mitochondrial homeostasis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial Adaptation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Novel Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Apr;28(4):250-260. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 27986466 Review.
-
Roux-en-y gastric bypass attenuates hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Gut. 2015 Apr;64(4):673-83. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-306748. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Gut. 2015. PMID: 24917551
-
A longitudinal study of whole body, tissue, and cellular physiology in a mouse model of fibrosing NASH with high fidelity to the human condition.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):G666-G680. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00213.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28232454 Free PMC article.
-
Nobiletin mitigates hepatocytes death, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in a murine model of NASH through modulating hepatic oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.J Nutr Biochem. 2022 Feb;100:108888. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108888. Epub 2021 Oct 22. J Nutr Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34695558
-
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and mechanisms by which it is ameliorated by activation of the CNC-bZIP transcription factor Nrf2.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Aug 1;188:221-261. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.06.226. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35728768 Review.
Cited by
-
Weight regain, but not weight loss exacerbates hepatic fibrosis during multiple weight cycling events in male mice.Eur J Nutr. 2024 Apr;63(3):965-976. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03326-w. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Eur J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38265751
-
Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 15;14(18):3796. doi: 10.3390/nu14183796. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145172 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Risk of Liver Disease in an Ovine Model of "PCOS Males".Biomedicines. 2022 May 31;10(6):1291. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061291. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740312 Free PMC article.
-
All about NASH: disease biology, targets, and opportunities on the road to NASH drugs.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 May;43(5):1101-1102. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00900-y. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35379932 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Investigating the Link between Ketogenic Diet, NAFLD, Mitochondria, and Oxidative Stress: A Narrative Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 8;12(5):1065. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051065. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

