Yuel: Improving the Generalizability of Structure-Free Compound-Protein Interaction Prediction
- PMID: 35103472
- PMCID: PMC9203246
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01531
Yuel: Improving the Generalizability of Structure-Free Compound-Protein Interaction Prediction
Abstract
Predicting binding affinities between small molecules and the protein target is at the core of computational drug screening and drug target identification. Deep learning-based approaches have recently been adapted to predict binding affinities and they claim to achieve high prediction accuracy in their tests; we show that these approaches do not generalize, that is, they fail to predict interactions between unknown proteins and unknown small molecules. To address these shortcomings, we develop a new compound-protein interaction predictor, Yuel, which predicts compound-protein interactions with a higher generalizability than the existing methods. Upon comprehensive tests on various data sets, we find that out of all the deep-learning approaches surveyed, Yuel manifests the best ability to predict interactions between unknown compounds and unknown proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
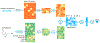
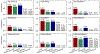
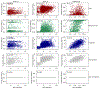
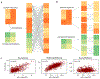
Similar articles
-
Biomedical Data and Deep Learning Computational Models for Predicting Compound-Protein Relations.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2022 Jul-Aug;19(4):2092-2110. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3069040. Epub 2022 Aug 8. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 33769935 Review.
-
Machine learning models for drug-target interactions: current knowledge and future directions.Drug Discov Today. 2020 Apr;25(4):748-756. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Drug Discov Today. 2020. PMID: 32171918 Review.
-
Leveraging Transfer Learning for Predicting Protein-Small Molecule Interactions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 14:2024.10.08.617219. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.08.617219. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39416112 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Explainable Deep Relational Networks for Predicting Compound-Protein Affinities and Contacts.J Chem Inf Model. 2021 Jan 25;61(1):46-66. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00866. Epub 2020 Dec 21. J Chem Inf Model. 2021. PMID: 33347301 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting drug-target interaction network using deep learning model.Comput Biol Chem. 2019 Jun;80:90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Comput Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30939415
Cited by
-
MISATO: machine learning dataset of protein-ligand complexes for structure-based drug discovery.Nat Comput Sci. 2024 May;4(5):367-378. doi: 10.1038/s43588-024-00627-2. Epub 2024 May 10. Nat Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 38730184 Free PMC article.
-
In silico protein function prediction: the rise of machine learning-based approaches.Med Rev (2021). 2023 Nov 29;3(6):487-510. doi: 10.1515/mr-2023-0038. eCollection 2023 Dec. Med Rev (2021). 2023. PMID: 38282798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CANDI: A Web Server for Predicting Molecular Targets and Pathways of Cannabis-Based Therapeutics.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:rs.3.rs-4744915. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4744915/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39149470 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Integrating QSAR modelling and deep learning in drug discovery: the emergence of deep QSAR.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Feb;23(2):141-155. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00832-0. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38066301 Review.
-
Whole proteome mapping of compound-protein interactions.Curr Res Chem Biol. 2022;2:100035. doi: 10.1016/j.crchbi.2022.100035. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Curr Res Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 38125869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drews J Drug Discovery: A Historical Perspective. Science. 2000, 287, 1960–1964. - PubMed
-
- Macarron R; Banks MN; Bojanic D; Burns DJ; Cirovic DA; Garyantes T; Green DVS; Hertzberg RP; Janzen WP; Paslay JW Impact of High-Throughput Screening in Biomedical Research. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2011, 10, 188–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

