Cytohesin-2/ARNO: A Novel Bridge Between Cell Migration and Immunoregulation in Synovial Fibroblasts
- PMID: 35095899
- PMCID: PMC8790574
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.809896
Cytohesin-2/ARNO: A Novel Bridge Between Cell Migration and Immunoregulation in Synovial Fibroblasts
Abstract
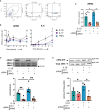
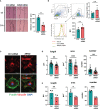
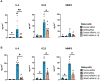
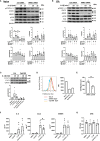
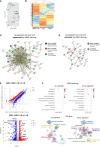
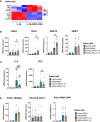
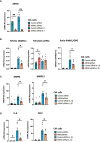
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor cytohesin-2 (ARNO) is a major activator of the small GTPase ARF6 that has been shown to play an important role(s) in cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton reorganization in various cell types and models of disease. Interestingly, dysregulated cell migration, in tandem with hyper-inflammatory responses, is one of the hallmarks associated with activated synovial fibroblasts (SFs) during chronic inflammatory joint diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis. The role of ARNO in this process has previously been unexplored but we hypothesized that the pro-inflammatory milieu of inflamed joints locally induces activation of ARNO-mediated pathways in SFs, promoting an invasive cell phenotype that ultimately leads to bone and cartilage damage. Thus, we used small interference RNA to investigate the impact of ARNO on the pathological migration and inflammatory responses of murine SFs, revealing a fully functional ARNO-ARF6 pathway which can be rapidly activated by IL-1β. Such signalling promotes cell migration and formation of focal adhesions. Unexpectedly, ARNO was also shown to modulate SF-inflammatory responses, dictating their precise cytokine and chemokine expression profile. Our results uncover a novel role for ARNO in SF-dependent inflammation, that potentially links pathogenic migration with initiation of local joint inflammation, offering new approaches for targeting the fibroblast compartment in chronic arthritis and joint disease.
Keywords: ARNO; arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis); cytohesin 2; inflammation; synovial fibroblast (FLS).
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Çil, Harnett and Pineda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ARL4D recruits cytohesin-2/ARNO to modulate actin remodeling.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4420-37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0149. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17804820 Free PMC article.
-
RLIP76 regulates Arf6-dependent cell spreading and migration by linking ARNO with activated R-Ras at recycling endosomes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Nov 27;467(4):785-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.064. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26498519 Free PMC article.
-
ARNO regulates VEGF-dependent tissue responses by stabilizing endothelial VEGFR-2 surface expression.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Jan 1;93(1):111-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr265. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22002459
-
Cytohesin-2/ARNO, through its interaction with focal adhesion adaptor protein paxillin, regulates preadipocyte migration via the downstream activation of Arf6.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 30;285(31):24270-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125658. Epub 2010 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20525696 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast biology. Role of synovial fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(5):361-7. doi: 10.1186/ar113. Epub 2000 Jun 8. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11094449 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel 3D spheroid model of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue incorporating fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and macrophages.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1188835. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188835. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37545512 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis and validation reveal CYTH4 as a potential prognostic biomarker in acute myeloid leukemia.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jan 16;27(3):103. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14236. eCollection 2024 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38298432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filer A, Bik M, Parsonage GN, Fitton J, Trebilcock E, Howlett K, et al. . Galectin 3 Induces a Distinctive Pattern of Cytokine and Chemokine Production in Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts via Selective Signaling Pathways. Arthritis Rheumatol (2009) 60(6):1604–14. doi: 10.1002/art.24574 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

